Did you know that 80% of Life Sciences companies are lagging behind in digitalizing their core business? For some, paper documentation is still piling up. For others, their new digital solutions are not yet fully utilized.
Get ahead in the digital race. Keep reading and learn how to revolutionize your organization’s digital capabilities for Quality management.
In this blog article, we discuss the challenges and benefits of going fully digital in the Life Sciences. We’ll do this by showcasing Scilife’s approach to digital transformation and how our innovative digital solutions can boost your organization’s productivity by up to 40%. Enhance your current Quality Management System (QMS) by digitally transforming these key areas:
- Documentation retrieval
- Data integrity and compliance
- Team collaboration
- Cost savings
- Improved compliance
- Enhanced decision-making
Scilife’s Smart QMS can help you maintain compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Recent studies (Lakshman & Stirling, 2018) show that 85% of respondents from companies in the Life Sciences industry:
- See tech companies as the driving force of digitalization in their industry, and 63% of them see these companies as possible cooperation partners within the next year.
- Companies such as Microsoft, Cisco, IBM, Amazon, and Google are among the world’s leading technology companies in the Life Sciences, leading digital transformation. Although biotech (69%) and MedTech (67%) saw strong drivers, they did not consider patient insurance to be one of the transformations.
- 46% of respondents have already been created or plan to be created in a CDO role that places responsibility for digitalization at the C-level.
- 24% of companies believe that digitalization has already or will have a significant impact on finding active ingredients and therapies for incurable or difficult-to-cure diseases.
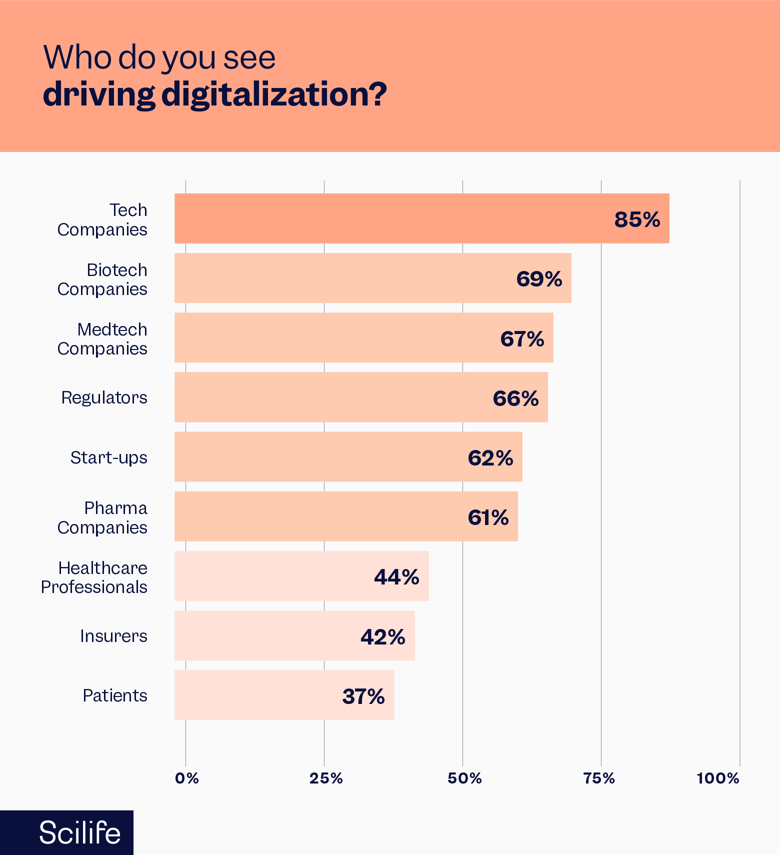
Source: KPMG - Digitalization in Life Sciences
Based on the projects implemented, the IT department is leading the industry with the highest number of implemented projects. However, Quality Assurance, procurement, and administration follow IT with more than 60% of implemented projects. Also, Quality has the highest number of projects that are planned and less percentage with no projects along with IT. In simple terms, don’t fall behind in the digital race, get ahead as soon as possible.
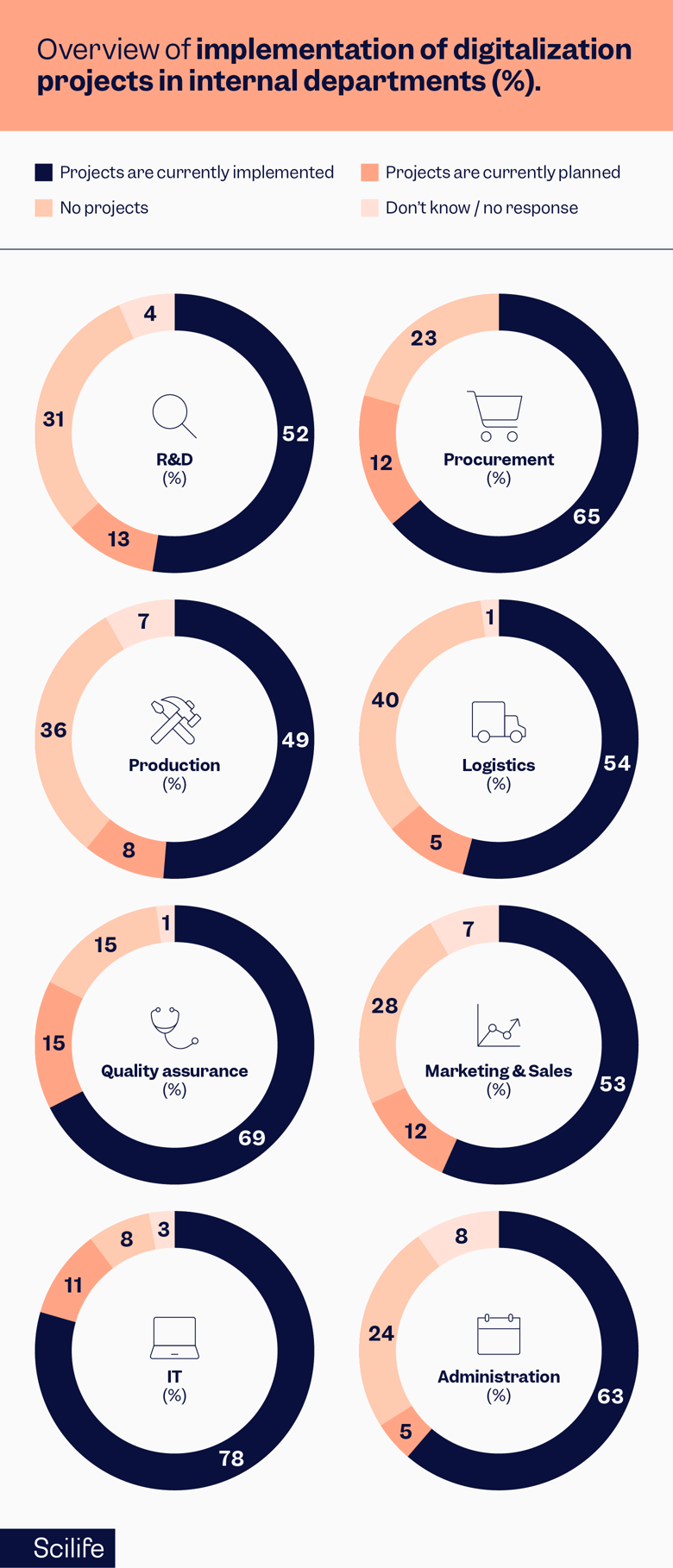
Source: KPMG - Digitalization in Life Sciences
Starting Your Digital Transformation
The first step towards digital transformation is to identify the current state of your company’s QMS and what needs to be digitized.
When you have gained insight into the current state of the company’s QMS and aspects, it is time to make a decision about which digitalization software and tools will best suit your company and your business processes once you have these inputs. It is important to create a comprehensive transformation plan before starting a digital transformation and to assess the readiness of the company to undergo the transformation.
Also, understanding a company’s current situation is essential before moving forward with digitalization to ensure you are getting ready to take the right steps.
You can use this comprehensive roadmap as a guide for your own digital transformation. Practical pieces of advice will help you implement each step, such as assessing your current state, deciding what your vision should be, and then implementing it.
Step 1: Assess the State of Your Quality Management System
A. Conduct an Analysis of the Status Quo
This first step involves assessing the current state of the QMS and identifying areas in need of digitization. This analysis involves a comprehensive review of documentation, processes, compliance with regulations, data management, and integration with other systems. The goal is to identify pain points, inefficiencies, and opportunities for digitization within the current QMS.
- Review existing documentation and processes:
Make sure to include standard operating procedures (SOPs), work instructions, and Quality records in this initial review. Identify areas where manual or paper-based processes are predominant. - Identify pain points and inefficiencies:
Engage stakeholders from all departments to gather feedback on the current QMS. Identify inefficiencies, pain points, and bottlenecks through interviews, surveys, or workshops. - Assess compliance with regulations and standards:
Evaluate the current QMS compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Identify any areas where digitalization could improve compliance. - Analyze data management and reporting:
Evaluate how data is captured, stored, and reported in the QMS. Assess the accuracy, accessibility, and timeliness of data; then identify opportunities for automation and improved data analytics. - Evaluate integration with other systems:
Assess how the current QMS integrates with other critical systems such as the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). Identify where integration gaps exist that could benefit from digitalization.
Following these steps to analyze the current state of your QMS will identify clear areas for digitization. This can help you develop a comprehensive plan for implementing digital transformation initiatives.
B. Define Digital Objectives and Key Performance Indicators
This step involves defining the objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) for digital transformation, which will serve as a benchmark for measuring progress. These objectives can include improving operational efficiency, enhancing data accuracy and accessibility, reducing compliance risks, and enabling better decision-making. The KPIs will help track progress and measure the success of digital transformation efforts.
Step 2: Define the Vision
A. Create a Roadmap for Digital Transformation
This step involves creating a roadmap for the digital transformation of the QMS, including timelines, milestones, and budgets. Throughout the transformation, your roadmap will provide a clear direction and help prioritize activities during the implementation process.
- Outline the specific steps, resources, and timeline required to digitize the identified areas
- Address potential challenges and dependencies
- Align with organizational goals
B. Identify Necessary Resources and Stakeholders
This involves identifying the needed resources and stakeholders to implement digital transformation, including IT professionals with expertise in digital solutions, Quality Assurance personnel who understand QMS requirements, and management support. Engaging key stakeholders throughout the process will help ensure alignment, collaboration, and collective ownership of digital transformation initiatives.
- Identify high-priority areas for digitization
Based on the conducted analysis, prioritize areas of the QMS that would benefit the most from digitization. This could include document control, training management, change control, deviation management, and CAPA processes. - Engage key stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders, including Quality Assurance personnel, IT professionals, process owners, and management, in the analysis process. Seek their input, address their concerns, and ensure their buy-in for digital transformation initiatives. - Consider technology options
Explore available technology solutions that can support the digitization of the identified areas within the QMS. Select the software that meets your needs and requirements.
C. Develop a Change Management Plan
This step involves developing a plan to manage the change associated with digital transformation, including:
- Communication strategies to address potential challenges and concerns during the transformation
- Training programs to upskill employees on new digital tools and processes
Stakeholder engagement - Ongoing support to facilitate a smooth adoption
Recognize that the digital transformation of the QMS will require changes in processes, roles, and responsibilities. A well-defined change management plan is essential to facilitate smooth adoption and minimize resistance.
Step 3: Execute the Plan
This involves deploying the digital solution and monitoring the progress against the objectives and KPIs. During this step, you will execute the digital transformation plan, deploy the chosen digital solutions, and implement the necessary process changes. This includes:
- Configuring and customizing the software
- Migrating data
- Training employees
Ensuring a smooth transition from the old system to the new digitized QMS
Regular monitoring and evaluation should occur to address any issues that arise and ensure that the implementation aligns with the defined objectives and KPIs.
Step 4: Monitor and Continuously Improve
This step involves continuously monitoring and improving the digital transformation to ensure that it meets the objectives and KPIs and remains aligned with the company’s goals and needs. Digital transformation is an ongoing process, and it is crucial to monitor the results and continuously improve the digitized QMS. You should regularly:
- Assess the performance
- Collect user feedback
- Identify areas for further optimization and enhancement
This iterative approach ensures that digital transformation remains effective, adapts to evolving needs, and delivers sustainable benefits over time.
Which Software is Best for You?
Deciding which software best suits your organization is one of the most critical and immediate decisions of your digital transformation journey. Make sure to identify the key features your company requires in your new digital QMS. Additionally, you can consider the following items while looking for the best option.
Further Reading: Guide to an Enterprise Quality Management Software Selection
- Creating a cross-functional team should include Quality managers at the executive, corporate, plant, and laboratory levels.
- Selecting the vendor via well-defined selection criteria:
- Functionality
- Cost
- Usability of the interface
- Centrally distributed vs. managed
- Technical features need to be set to mandatory, priority level, or lower
- Infrastructure (on-site vs. net-based vs. cloud-based)
- Browser specific vs. browser agnostic
- Integration or interoperability with other platforms such as CAPA should integrate with ERP, CRM, SPC (Statistical Process Control), and other systems
- Security
- Optional pilot program
- Does the environment ensure the fulfillment of compliance requirements of your
- organization for highly sensitive data?
Benefits of Digital Transformation
Digitalization has revolutionized the landscape of QMS in various industries, including pharmaceuticals. By harnessing new technologies and embracing a culture of Quality, organizations can achieve remarkable advancements in efficiency, compliance, and decision-making. As organizations embrace the transformative power of digital technologies, they unlock long-term advantages such as increased efficiency, speed to market, and sustained compliance, ultimately cultivating a culture of Quality that permeates the entire organization.
A recent study has shown that Quality 4.0 provides many more benefits when compared to traditional Quality system elements.

- Efficient determination of product Quality through new technologies and the integration of prescriptive analytics
- Real-time visibility, effective data collation, and agile decision-making
- Higher connectivity standards for enterprise QMS and real-time data collection through connectivity with manufacturing and laboratory technologies
- Streamlined and synthesized Quality activities for better compliance and efficiency
- Improved connectivity with internal and external environments through augmented reality, virtual reality, software applications, enhancing collaboration, and data management
- Scalability and reconciliation of processes, competencies, and practices
- Simplified data collection, visualization, and collaboration through application development improving efficiency and productivity
- Increased customer satisfaction through personalized and customizable products and services
- Enhancing supply chain management through better collaboration and transparency mitigates potential risks
- Higher Quality standards and reduced defects through advanced monitoring and control systems
- Enhancing employee engagement and empowerment through skill development and competency
- Improved compliance through automated activities and data collection
- A Quality culture that permeates the entire organization, driven by digital transformation
- Improved data management, enhanced collaboration, and increased agility
- Utilization of Big Data, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain
- Digital transformation overall streamlines QMS, improves compliance, and reduces costs
Common Challenges (and How to Overcome Them)
The digital transformation of organizations has become a vital endeavor in today’s technology-driven landscape. Despite this and its valuable benefits, there are still challenges to overcome. To achieve a smooth and successful digital transformation journey, it is essential to understand and proactively address these obstacles. Now let’s explore some of the most common challenges that organizations face before, during, and after a digital transformation, and provide practical strategies for overcoming them.
Resistance to Change
Digital transformation is often accompanied by resistance to change by staff, which is one of the most common challenges. Despite the many advantages of digital transformation and new technologies and processes, some employees may be hesitant due to fears of job loss, lack of familiarity, or perceived complexity. Using change management is one of the most effective methods to overcome resistance. It helps to alleviate employee concerns if there is clear communication about the benefits of digital transformation, and if a culture of continuous learning is fostered, as well as involving them in the process. Training programs, workshops, and internal champions can all help to drive acceptance and encourage the adoption of new technologies.
Lack of Digital Skills
Digital transformation requires a new set of skills and expertise for almost every company which may not be readily available. A lack of skills can impede the implementation and optimization of digital initiatives. Empower employees with the necessary digital skills by investing in upskilling and reskilling programs. Work with external partners, training institutions, or online learning platforms to provide targeted training. To facilitate skill development, cross-functional teams should be encouraged to collaborate and share knowledge.
Data Privacy and Security
You may experience an increase in cybersecurity risks and privacy concerns as your processes become more dependent on digital tools and collect large amounts of data. Data breaches, regulatory compliance issues, and the protection of sensitive information are some of the things that can hinder digital transformation moving forward. Make sure to implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular audits of the security system. Identify and develop a comprehensive data protection strategy aligned with the industry’s standards and regulations. Through training programs and strict policies for handling and sharing data, you can foster a culture of security awareness among employees by encouraging them to be aware of security risks.
Legacy Systems and Infrastructure
Digital transformation can pose significant challenges when legacy systems and infrastructure are outdated. Legacy systems may not be capable of supporting modern digital initiatives because they lack flexibility, scalability, and compatibility. Make sure to thoroughly evaluate your existing systems, identify any areas that need to be upgraded or replaced, and then migrate or adopt a phased approach to minimize disruptions.
Change in Organizational Culture
An organization’s digital transformation efforts can be hindered by traditional hierarchical structures and siloed departments. You should foster a culture of innovation, openness, and collaboration throughout the transformation. By encouraging cross-functional collaboration and information sharing, you can break down the so-called silos. Foster an environment that promotes innovation, openness, and collaboration across departments. Leaders must provide leadership support and lead by example to enable employees to experiment, take calculated risks, and embrace continuous learning in order to drive cultural change within an organization.
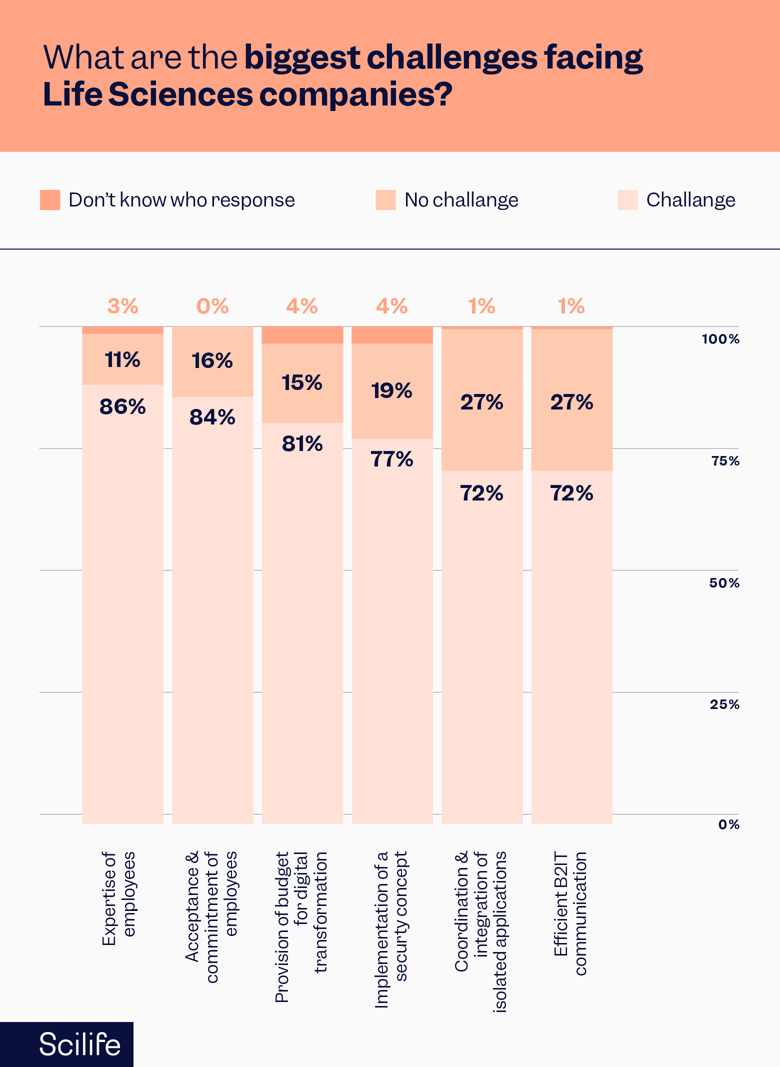
A recent study by KPMG confirmed that the three biggest challenges for more than 80% of companies are a lack of digital competencies, employee acceptance, and approved budgets for digital transformation.
Similarly, another recent study by Deloitte showed the four biggest challenges are cash, capacity, competency, and control for digital transformation.
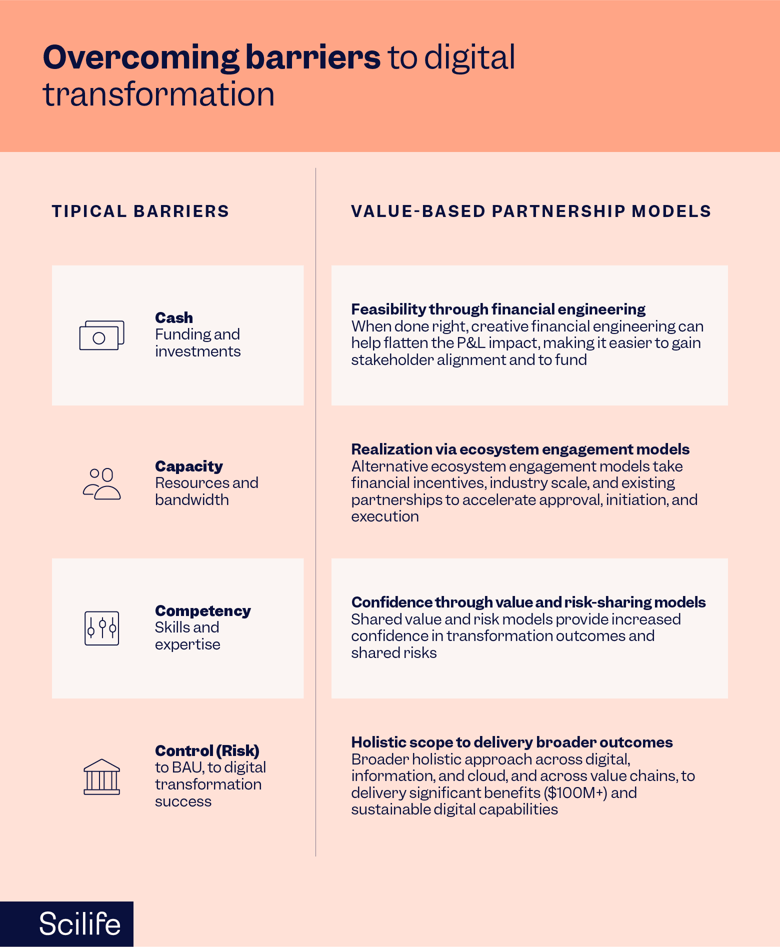
Source: Deloitte
After the Transition: What’s Next?
We as humans are used to doing everything manually. Only in recent years we have started to rapidly digitize processes as much as possible. Maybe you’re at the very beginning of the digitalization journey or you’ve already transformed a couple of processes. But progress never stops. There is always room for continuous improvement and digitalization. Let’s see what’s next after the transition is complete. Check out these key practices that you can undertake after the digitalization. Based on the Deloitte report on the biopharma factory of tomorrow, building smart factories requires more than just enabling digital innovations. It’s about transforming infrastructure and culture within manufacturing organizations, including:
- Building connectivity
Shifting away from siloed manufacturing processes towards a connected manufacturing ecosystem that allows the free flow of information, data, and actionable insights. - Changing innovation mindsets
Consider how digital technologies can augment human capabilities and change the execution of processes through a digital-to-be-digital mindset. - Encouraging the art of the possible
Making plant owners aware of the tangible value of digital innovation by encouraging digital innovation pilots value of plant. - Productize and scale digital innovation
Identify and leverage external capabilities through ecosystems and alliances rather than disparate digitalization efforts and viewing digital innovation as an in-house engineering problem.

Conclusions, Takeaways, Final Concerns
As a result of the digital transformation, the pharmaceutical industry has experienced significant advancements and opportunities. As pharma goes through its digital transformation journey, there are challenges to overcome. As the industry deals with sensitive patient information and valuable intellectual property, data security and privacy are major concerns. Building trust and protecting confidential data requires the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures and adherence to rigorous regulatory frameworks.
The successful implementation of digital technologies requires an understanding of the pharmaceutical industry’s specific needs and challenges. Integrating digital solutions into existing processes and workflows is another crucial aspect. To drive truly effective change, align digital initiatives with your business strategy and foster a culture of collaboration and innovation. Using analytics and data-driven insights is an important takeaway as the industry moves forward. The data-driven approach enables better decisions throughout the product lifecycle.
It has been shown that digital transformation can significantly improve patient care, drive innovation, and optimize business operations in the pharmaceutical industry. Pharma companies can realize the full benefits of digital technologies by addressing challenges related to data security, integration, and user experience. Embracing a culture of continuous learning, adaptation, and collaboration will be crucial to navigating the rapidly evolving landscape of digital transformation and shaping a future where technology and healthcare converge to improve outcomes.
Discover how Scilife smart QMS can help you achieve this transition
Moving Towards Smart Quality
Taking advantage of technology to achieve Smart Quality is the next step in the digital transformation of the Life Sciences. The idea of being Smart about Quality is to maximize Quality Control processes and ensure that products are safe and effective by integrating advanced analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence.
Pharmaceutical companies can identify and resolve Quality issues more effectively by using Big Data and data analytics. To detect anomalies and deviations from established Quality parameters, advanced analytics can analyze large volumes of data from various sources, including production equipment, environmental sensors, and Quality Control systems. Through this proactive approach, product recall risks are minimized, processes are enhanced, and patient safety is ultimately protected.
To streamline Quality Control processes and reduce human error, automation is crucial. As a result of robotic process automation (RPA), Quality Control professionals can focus on more critical and complex tasks instead of repetitive tasks such as data entry, sample testing, and documentation. Additionally, intelligent automation, including machine learning algorithms, can be used to optimize equipment performance and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance.
Especially in the pharmaceutical industry, artificial intelligence can analyze complex datasets, identify patterns, and predict potential Quality issues. And machine learning models can identify correlations between raw materials, manufacturing parameters, and product Quality, allowing manufacturers to improve processes and prevent defects based on data. Finally, by integrating advanced analytics, automation, and artificial intelligence, pharmaceutical companies can embrace Smart Quality as the future of Quality Control. Moreover, the industry can increase transparency and efficiency by incorporating digital technologies into supply chain management.
Ultimately, to achieve Smart Quality, collaboration, knowledge sharing, and continuous improvement must be fostered, resulting in a safer and more effective pharmaceutical industry.