The world of medical devices is steeped in regulations - you can't say medical devices without saying compliance. In this world of medical device regulations, compliance is critical. It ensures the safety and efficacy of products entering the market and, most importantly, the protection of patients.
Over time, various regulatory frameworks have been established globally to uphold these standards. In the world of regulatory giants, the Quality System Regulation (QSR) in the United States and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 13485 have long been kings. And recent developments signal a shift towards harmonization between these frameworks, heralding the advent of the U.S.'s Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR).
The QMSR was first proposed in February of 2022 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the applause from the medical device industry thundered. The final rule on the QMSR was issued January 31st, 2024, with an implementation date of February 2nd, 2026 – by this date, all manufacturers in the U.S. must comply with the requirements of the QMSR. Until then, compliance with the current QS Regulation is sufficient.
This article delves into the implications of QMSR, the harmonization between QSR and ISO 13485, and how medical device companies can prepare for this transition.
What Does the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) Imply? And How Does It Differ from the QSR?
The Quality System Regulation (QSR), established by the FDA, outlines the requirements for medical device manufacturers to ensure product quality and safety.
Likewise, ISO 13485 is an internationally recognized standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system specific to medical devices. The critical difference lies in their scope and applicability: while QSR is U.S.-centric, ISO 13485 has global recognition (although it is most widely implemented in the European Union).
The emergence of the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) signifies a convergence between these two frameworks. QMSR aims to streamline regulatory requirements, aligning U.S. regulations more closely with international standards, such as ISO 13485. This alignment facilitates smoother market access for manufacturers operating in both domestic and international markets, reducing compliance burdens and enhancing efficiency.
Why Harmonize?
The harmonization between QSR and ISO 13485 addresses several challenges medical device manufacturers face. Historically, navigating the differences between regulatory regimes has been complex and resource-intensive. Misalignment between QSR and international standards often led to duplicative efforts, increased compliance costs, and delayed market entry. Manufacturers looking to enter the U.S. have been unable to fully leverage their ISO 13485 compliance, while U.S. manufacturers looking to enter the E.U. have needed double compliance to align their QSR-compliant quality systems to ISO 13485.
Harmonization offers a strategic solution to mitigate these challenges while fostering several key benefits:
- Global Market Access: By aligning regulatory requirements, harmonization promotes mutual recognition of standards, facilitating market access across diverse regions.
- Enhanced Consistency: Harmonization fosters consistency and clarity in regulatory expectations, reducing ambiguity and interpretation discrepancies.
- Operational Efficiency: Harmonization streamlines processes, eliminates redundancies, and optimizes resource allocation, enabling manufacturers to focus on innovation and product development.
How Does This Harmonization Affect Medical Device Companies?
The harmonization between QSR and ISO 13485 has profound implications for medical device companies. Primarily, it necessitates a shift in compliance strategies and quality management practices. Companies operating in the U.S. must align their quality systems with the revised QMSR requirements, ensuring seamless transition and continued compliance. Conversely, companies adhering to ISO 13485 will find greater alignment with QMSR, potentially reducing the need for redundant procedures and documentation.
Moreover, harmonization opens up opportunities for manufacturers to expand their market presence. Compliance with internationally recognized standards such as ISO 13485 enhances credibility and facilitates market entry into regions with stringent regulatory requirements. By harmonizing with global standards, medical device companies can streamline their regulatory processes, accelerate product approvals, and gain a competitive edge in the worldwide marketplace.
Achieving compliance with QMSR requires careful planning and resource allocation. Companies must invest in training, infrastructure, and process optimization to meet the revised regulatory requirements. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and adaptation to evolving regulatory landscapes are essential to maintain compliance and adapt to market dynamics.
How Can Medical Device Companies Prepare for the QMSR?
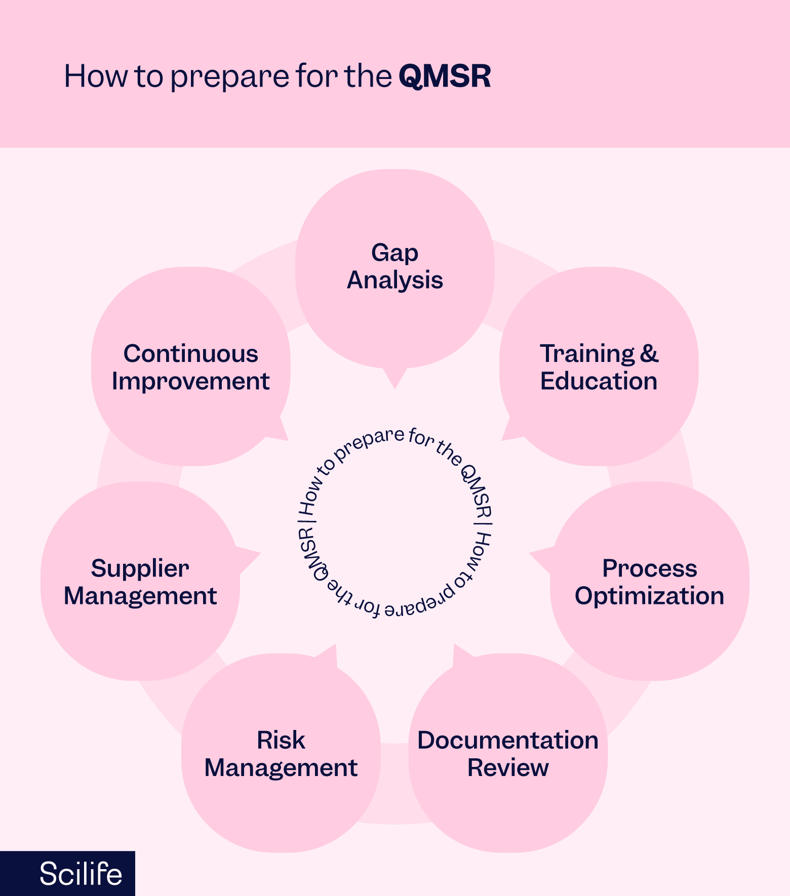
Preparing for QMSR requires a comprehensive approach encompassing several vital steps:
Gap Analysis
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing quality management systems and processes to identify gaps and areas requiring improvement. This includes inspections processes as well, since the FDA will implement new processes to comply with the updated regulation. If manufacturers already comply with ISO 13485, familiarizing themselves with the additional sections of the QMSR that goes beyond ISO 13485 and how they can achieve compliance is a great start. If manufacturers are not ISO 13485 compliant, a more thorough and comprehensive gap analysis is needed and focusing on the similarities and differences between 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485 is a good place to start. In particular, taking a long stare on risk management activities is recommended, as both ISO 13485 and the QMSR places heavy emphasis on risk management.
Training and Education
Ensure that employees are adequately trained on the revised regulatory requirements and best practices for compliance.
Process Optimization
Streamline and optimize internal processes to align with QMSR requirements while minimizing redundancy and inefficiency.
Documentation Review
Review and update documentation, including quality manuals, procedures, and records, to ensure alignment with QMSR standards.
Risk Management
Enhance risk management processes to identify, assess, and mitigate product quality risks and regulatory compliance risks.
Supplier Management
Strengthen supplier quality management processes to ensure the quality and compliance of materials and components sourced from external suppliers.
Continuous Improvement
Establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement of quality management systems to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and market dynamics.
By proactively addressing these aspects, medical device companies can effectively prepare for the transition to QMSR and position themselves for sustained success in the evolving regulatory landscape.
Conclusion
The harmonization between QSR and ISO 13485 through the introduction of QMSR represents a significant milestone in regulating medical devices. By aligning regulatory requirements and promoting global standards, QMSR aims to enhance efficiency, consistency, and market access for manufacturers. This harmonization brings us one step closer to global regulatory standards.
While it presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for companies to streamline their operations, expand market presence, and drive innovation. Through proactive preparation, including gap analysis, training, process optimization, and continuous improvement, medical device companies can navigate the complexities of QMSR and emerge stronger in the competitive global marketplace.
Discover how Scilife smart QMS for Medical Devices can help you be prepared for QMSR.