EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium

Data integrity within the life sciences environment is crucial for maintaining the quality and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and ultimately safeguarding product quality and patient safety.
Data Integrity refers to the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data throughout its lifecycle, ensuring that data is attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate (ALCOA), as well as complete, consistent, enduring, and available (ALCOA+).
Many components contribute to compliance, from the generation and processing of data to its storage and destruction. To ensure data integrity, companies are expected to establish a comprehensive ‘Data Integrity Program’.
The Data Integrity Program should include a plan to assess and remediate existing quality processes and systems, with a focus on addressing compliance gaps and managing responsibilities, remediation activities, and timelines.
Unfortunately, health authority inspectors continue to uncover violations of data integrity in life science companies due to systematic failures. Despite the fact that data integrity problems don't only affect Quality Control, many of these problems happen in QC labs.
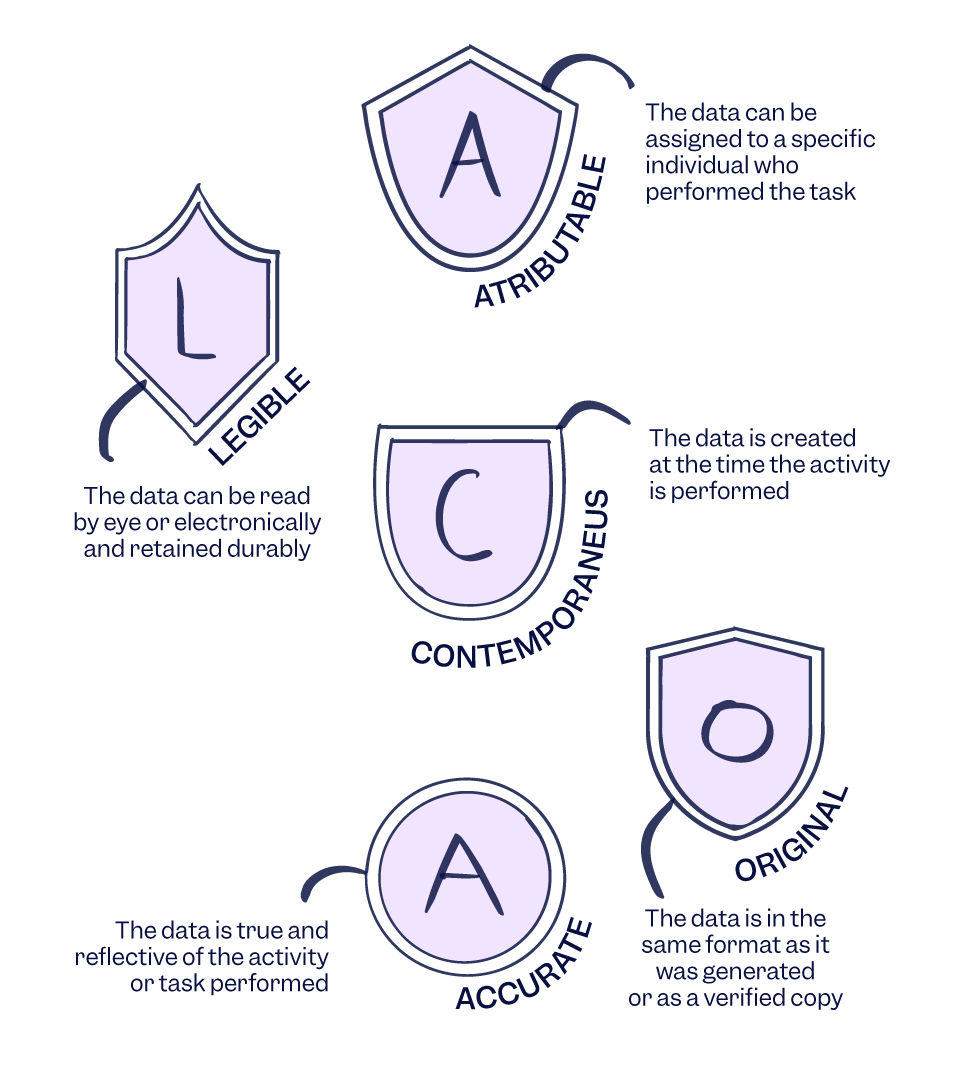
When data integrity is compromised, serious consequences can occur, including incorrect decisions being made, frequent inspections, suspension of approvals, import bans, recalls, criminal prosecutions, and reputational damage.
The reasons for failure range from occasional errors being made in not adequately following SOPs, occasional falsification of dates of sign off and transcription of data from post-it notes, backdating, to data manipulation and falsification.
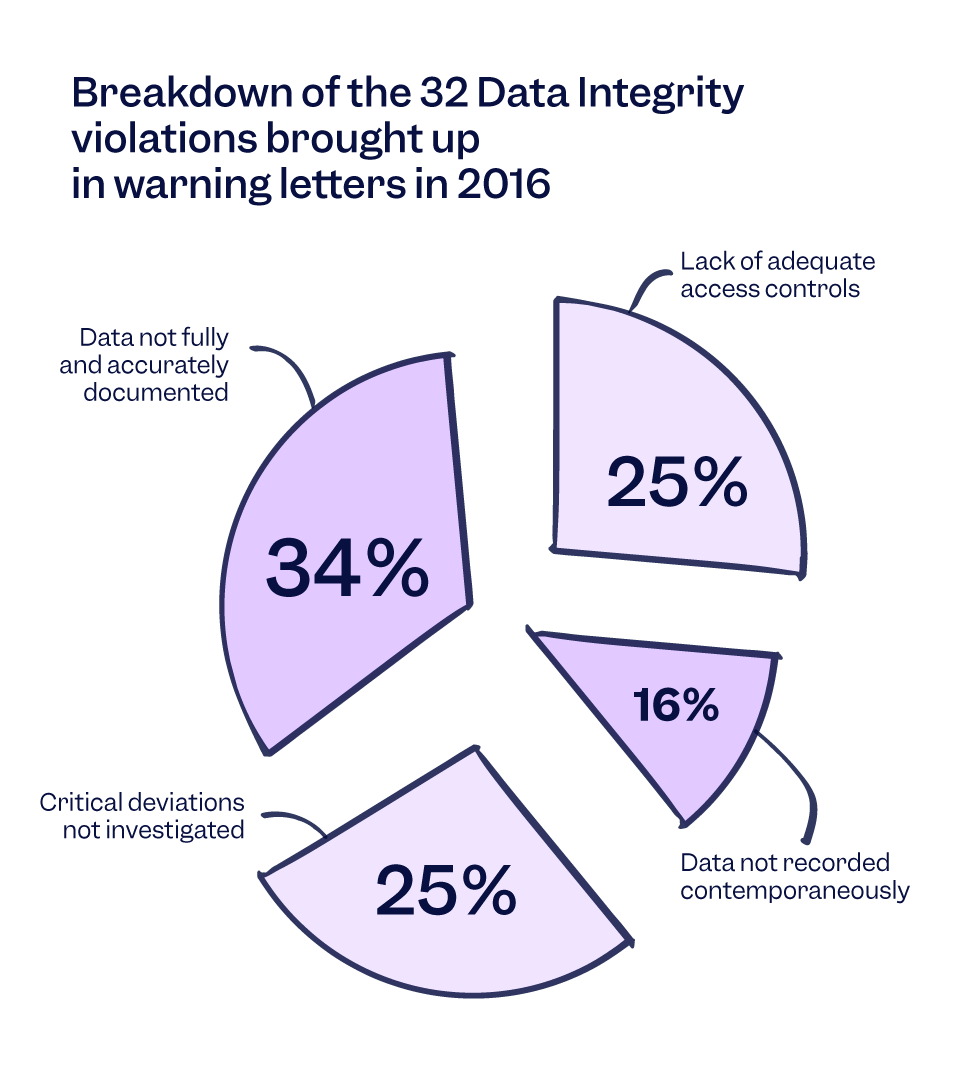
For example, Warning Letters from 2016 show that most common data integrity violations are due to data not being fully and accurately documented, which accounted for 34 per cent of the violations.
In order to effectively remediate these issues, digital technologies must be embraced in key areas, automating processes, reducing the need for manual data entry, and reducing transcription errors and intentional falsifications. Automating processes and ensuring best work practices, such as collecting data from interfaced instruments, can be accomplished with digital technologies.

When organizations prioritize accurate and transparent documentation of their data, it instills confidence in investors, partners, and customers. Stakeholders can trust that the information they rely on is not only secure but also reliable, fostering stronger relationships and enhancing the organization's reputation within the industry.
Accurate and well-documented data serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, empowering teams with reliable insights. This, in turn, leads to more strategic and effective decision-making, enabling organizations in the life sciences sector to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving landscape.
By adhering to established data integrity protocols, businesses not only avoid legal ramifications but also position themselves as responsible and trustworthy entities in the eyes of regulatory bodies, reinforcing their commitment to maintaining the highest standards in data management.
Robust data integrity practices facilitate secure data sharing, fostering collaboration across institutions and researchers. Shared data can not only lead to accelerated innovation and improved outcomes in research and patient care but also holds the potential to uncover novel patterns and trends.
Emphasizing data integrity promotes a culture of continuous improvement, quality, and accountability. This approach empowers organizations to enhance agility, swiftly adapting to evolving regulations or market demands, thereby positioning themselves for sustained success in a dynamic environment.
By implementing robust data documentation and access control measures, organizations can fortify themselves against unauthorized access, tampering, and potential loss of critical information. This not only safeguards sensitive data but also strengthens the overall cybersecurity posture of the business.
One application of best practices of data integrity is in Smart Laboratories.
Traditional laboratories face challenges in ensuring data integrity, optimizing workflows, and accelerating discovery and development processes. Manual processes, data silos, and the potential for errors hinder efficiency and compliance.
With a Smart Laboratory solution, conventional labs will be transformed into agile, efficient, and digitally integrated spaces, setting the stage for the advancement of scientific research and fast quality control in the future.
Integrated IoT sensors will collect real-time data seamlessly, while robotic assistants automate tedious analytical tasks. A centralized hub that integrates insights will be backed by AI-powered analytics.
Data integrity will be safeguarded by blockchain technology. In this digitized environment, experiments will be carried out at a rapid pace, and collaborative efforts will flourish. With this Smart Laboratory, today's scientific inquiry will take on a new dimension where discovery knows no bounds with enhanced efficiency, resource optimization, and a future-ready mindset.


Life sciences rely heavily on data integrity for quality, compliance, and patient safety. Building trust and fortifying against cyber threats will be made possible by maintaining data integrity. An organization that embraces data integrity is more than just compliant; it is an organization that strives for excellence, empowering businesses to make intelligent decisions based on data.
There are still threats associated with digital transformation that will require strategic attention. Incorporating novel technologies is challenging. Organizations must invest in the right people, processes, and technology to ensure their data is safe and secure. Cybersecurity must be a priority, and businesses should be proactive in their approach to protecting their data.
Explore what lies at the forefront of innovation and quality in life sciences.
EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium
US Office
Scilife Inc.
228 E 45th St. RM 9E
New York, NY 10017
EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium
US Office
Scilife Inc.
228 E 45th St. RM 9E
New York, NY 10017
Copyright 2025 Scilife N.V. All rights reserved.