EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium

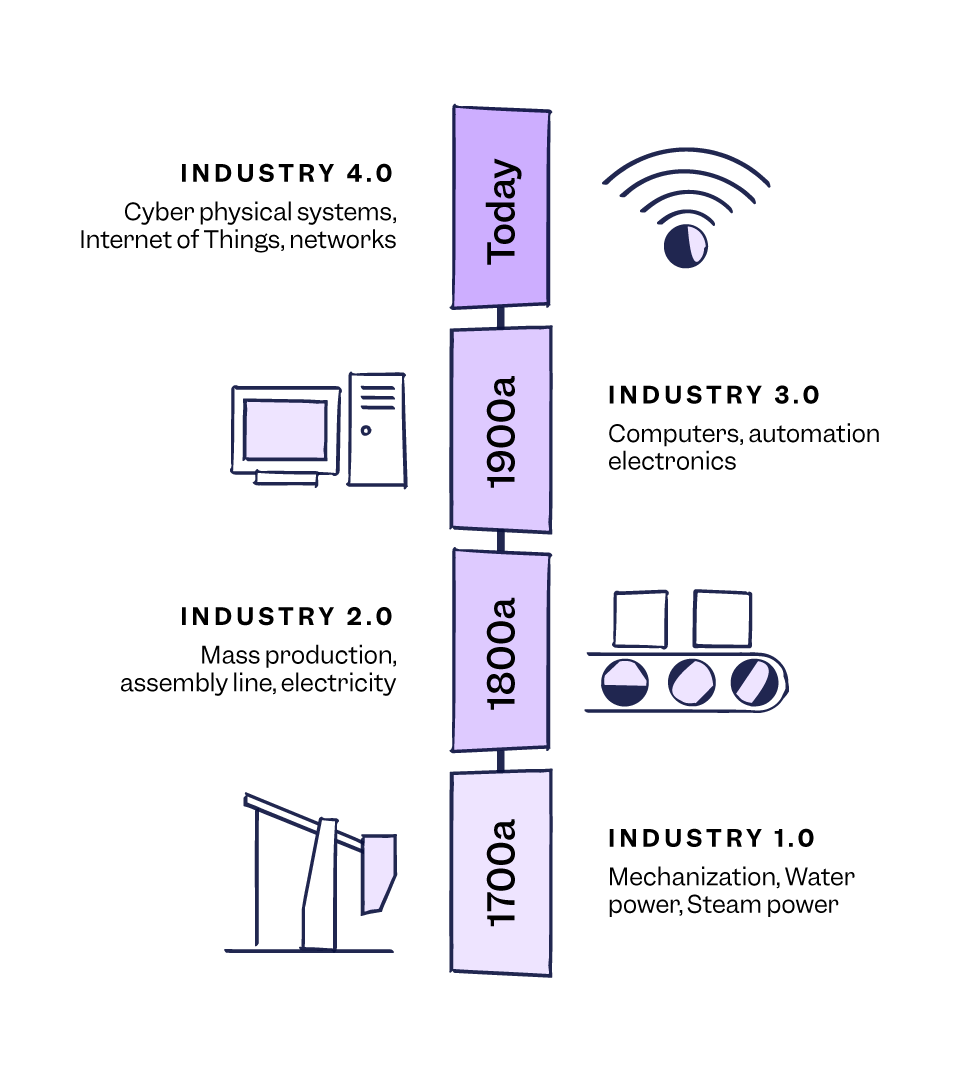
In Industry 4.0, manufacturing environments undergo transformations driven by global changes and disruptive technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Deep Learning, and the Internet of Things. Coined in 2011, at the Hannover Messe, Germany’s most important industrial fair, Industry 4.0 integrates information technologies, creating smart systems fueled by data and machine learning for more flexible and efficient working environments, optimizing processes in real-time.
As opposed to the fourth industrial revolution, Quality 4.0 focuses on maximizing quality culture, collaboration, competency and leadership, within a digital environment.
In Quality 4.0, quality professionals improve quality management by using the digital tools they have available today and understanding how to apply those tools effectively. In the face of digital disruption, quality professionals are becoming navigators rather than enforcers. They must be able to anticipate the digital disruption, understand the implications, and provide guidance and direction to their organizations in order to ensure that they can adapt and thrive.
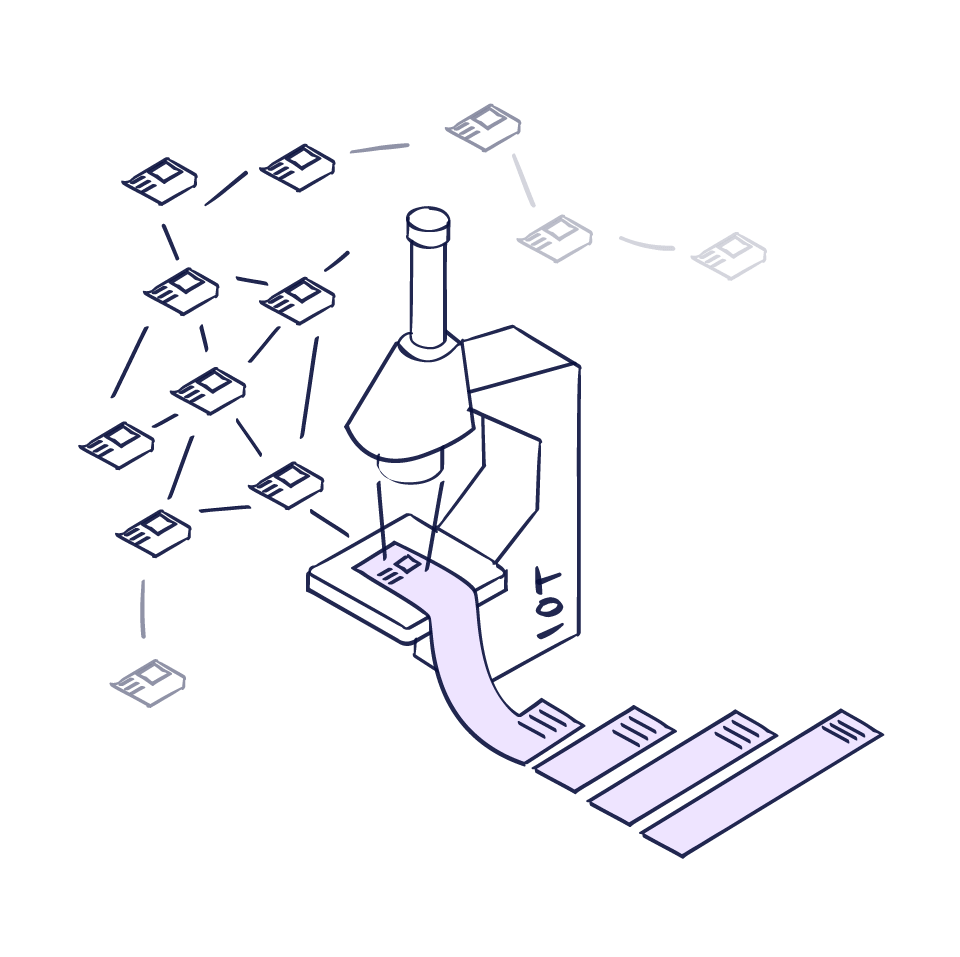
For example, stored equipment data is used to run algorithms to understand how any equipment works. It allows the generation of plausible scenarios of equipment malfunction, thereby reducing the possibility of production downtime losses.
Quality management can also be improved through the use of Internet of Things (IoT) and sensor technologies. These technologies provide a continuous stream of data from various stages of production and usage, which provides useful insights for predictive analytics. Therefore, organizations can optimize processes and predict quality issues using more robust models.
Cross-functional collaboration of subject matter experts is another trend in quality management. Team members from different departments, including production, R&D, and data analytics, collaborate on developing predictive analytics models in this approach. Collaboration ensures a comprehensive understanding of the entire value chain, leading to more accurate predictions and more effective quality management.

The current quality management systems are analytics-driven. They display metrics, KPIs, and trends on dashboards. Forecasts can be provided to facilitate decision-making. This reduces downtime and increases productivity.
As technology advances, companies will be able to monitor their operations in real-time, identify potential issues before they occur, and make decisions based on more accurate data.
It is likely that in the future, eQMS will guide us towards better management, and that it will even do so autonomously by learning how to anticipate potential issues and take the best decisions for different situations as they arise.
Industry 4.0 and Quality 4.0 will probably become obsolete in the future as work environments become increasingly connected, intelligent systems become widespread, and processes become automated.
Powered by data and predictive analytics, eQMS will make more accurate predictions, respond to changing conditions quicker, make smarter decisions, implement smoother processes, reduce costs, and accelerate innovation.
One top application of Industry 4.0 and Quality 4.0 in which manufacturers are finding value is in advanced predictive maintenance.
Traditionally, maintenance methods rely heavily on corrective maintenance, which is reactive in nature, in which equipment is used until it fails, and then repaired or restored to its original condition.
Failures are unpredictable in terms of when they occur and how long they will last, so a company cannot prepare for such events, leading to potentially costly consequences.
In contrast, predictive maintenance strategies based on machine learning algorithms are increasingly being utilized to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance ahead
of time.
By collecting data over time, patterns can be identified to predict and prevent failures, ultimately increasing reliability, reducing maintenance, and increasing equipment availability.


Life sciences is experiencing a transformational era. Industry 4.0 enables efficient, agile manufacturing, providing the opportunity to reduce costs and accelerate time-to-market. Quality 4.0 uses advanced technology to foster continuous improvement through proactive quality monitoring. As a result, the industry gains a competitive edge in delivering superior products efficiently through the synergy of these advancements.
Explore what lies at the forefront of innovation and quality in life sciences.
EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium
US Office
Scilife Inc.
228 E 45th St. RM 9E
New York, NY 10017
PRODUCT
RESOURCES
COMPANY
Contact Us
EMEA Office
Louizalaan 489
1050 Brussels
Belgium
US Office
Scilife Inc.
228 E 45th St. RM 9E
New York, NY 10017
Copyright 2025 Scilife N.V. All rights reserved.