In life sciences, one of the most heard terms is nonconformance management, or nonconformity or NC management. To utilize and maintain an ideal NC management process, first, you need to understand what it is for and what are the risks and costs if it doesn’t work properly.
Nonconformance management in life sciences aims to identify, document, investigate, and resolve the events that occur in an organization’s processes, products, or services. The crucial step of resolving a nonconformance is to address the problem, prevent future nonconformances from recurrence, and, of course continuously improve the organization’s processes.
Today, we’ll delve into the details of what nonconformance is, the different types of NCs, their impact on your business, and how to properly handle it. Additionally, we’ll discuss how to avoid nonconformances and the role of QMS software in streamlining nonconformance processes.
Why nonconformance management in life sciences matters
Nonconformances are inevitable in the life sciences, but unmanaged nonconformances are costly. From patient safety risks and regulatory findings to production delays and recalls, ineffective nonconformance management can quickly escalate into major compliance and business issues.
Nonconformance management provides a structured way to identify, document, investigate, and resolve deviations from requirements. When done well, it not only restores compliance but also drives continuous improvement across processes, products, and services. This article explains what nonconformance management is, and how life sciences organizations can master it at scale.
Let’s jump straight into the definition of nonconformance.
What is nonconformance?
A nonconformance can be defined as negligence or an unfavorable occurrence that happened to the product, process, or anywhere in the QMS. A failure to meet specified requirements.
For example, not using the management system properly or not following the SOPs can lead to nonconforming products. These requirements may be internal (company procedures, SOPs, quality standards) or external (regulatory or legal requirements).
In quality management systems specifically, nonconformance refers to any deviation that compromises compliance, safety, quality, or effectiveness.
Nonconformances can be generated by an anomaly during the execution of an activity (human error, technical problem, etc.), by the occurrence of an external event that compromises the quality of the service (weather conditions, foreign object, contamination, etc.), or by the inadequacy of the operating procedure to the expected results.
Regulatory requirements for nonconformance management in life sciences
Nonconformance management is required by multiple regulations and standards, including:
- ISO 9001:2015 (Clause 10.2)
- ISO 9000:2015 (Clause 3.6.9)
- ISO 13485:2016 (Clause 8.3)
- FDA 21 CFR Part 820
- GxP and GDP guidelines
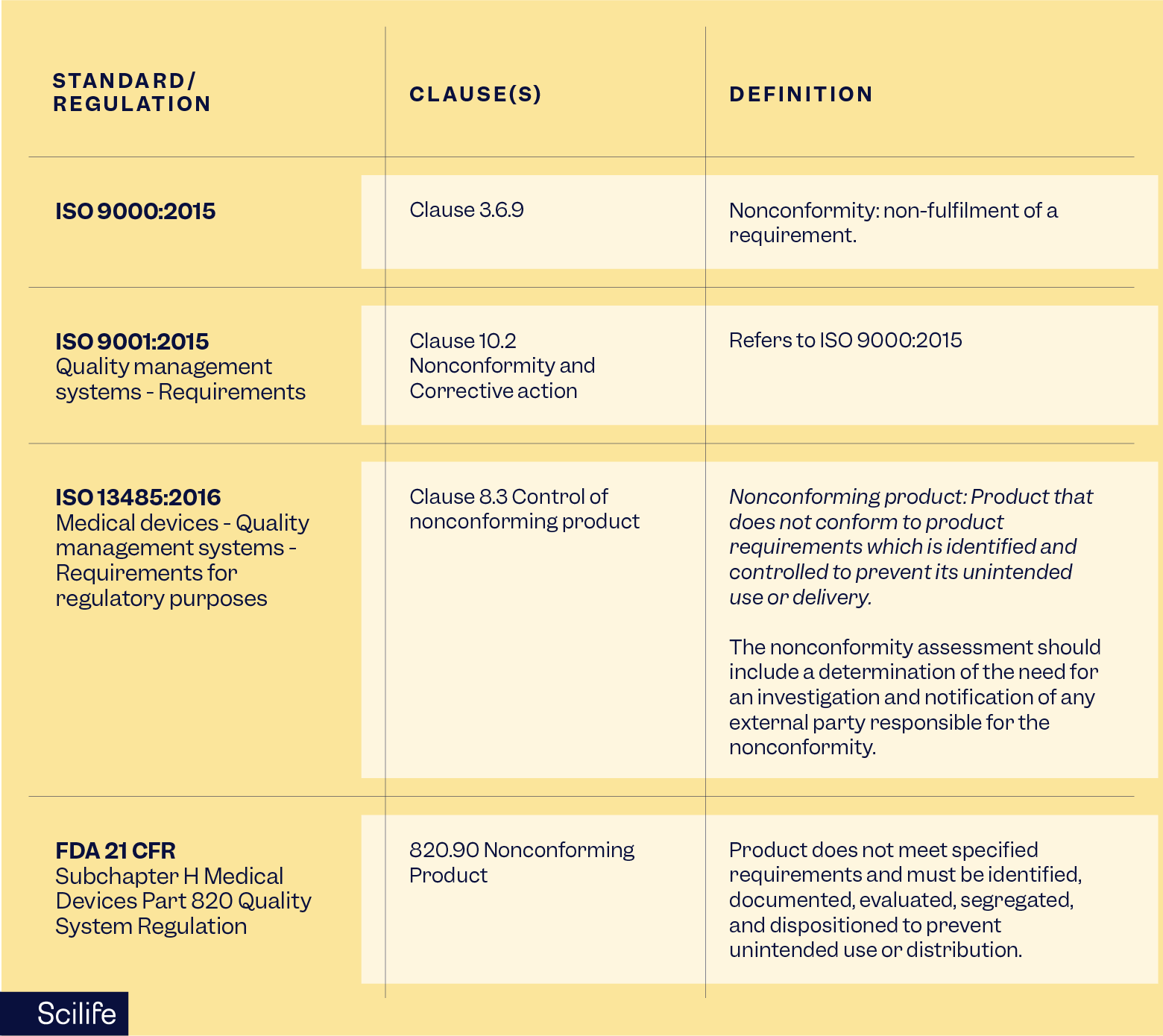
Regulators expect documented processes, timely investigations, effective corrective actions, and evidence of continuous improvement.
To comply with regulatory requirements such as FDA 21 CFR Part 820, medical device manufacturers, initial importers, and other organizations involved in producing and distributing devices for sale in the U.S. must register their establishments with the FDA to ensure that they have accurate information about all parties involved in the production and distribution of medical devices.
Establishments must use the FDA’s Unified Registration and Listing System (FURLS) to complete their registration electronically. Once registered, establishments must list all medical devices they manufacture, prepare, propagate, compound, assemble, or process for commercial distribution in the US.
While registration itself does not prevent quality issues, it forms part of the broader regulatory framework that governs how nonconforming products under FDA 21 CFR 820 must be identified, controlled, and dispositioned.
Within a quality management system, a nonconformance is defined as the failure to meet a requirement—whether that requirement is internal (such as company procedures or SOPs) or external (such as regulatory or standard-based requirements). In this context, organizations may encounter an ISO 13485 nonconformity related to product quality, process control, or documentation, or an ISO 9001 nonconformance related to the effectiveness of the management system itself.
Regardless of severity, nonconformances can impact product quality, patient safety, or regulatory compliance and therefore require timely evaluation and action. Minor nonconformances may be addressed through correction, while major or recurring issues typically require corrective action to prevent recurrence. For this reason, ISO 9001 Clause 10.2 emphasizes a structured approach to reacting to nonconformances and using them as opportunities for continuous improvement.
Recommended learning: Using risk-based thinking to manage nonconformities and deviations.
Nonconformance vs nonconformity, or NC
In the industry, nonconformances are also referred to as:
- Nonconformity
- Non-conformity
- NCs
According to ISO standards, conformity means fulfillment of a requirement, while nonconformance indicates a failure to meet that requirement.
The industry often uses nonconformance as a synonymous term, but ISO’s official vocabulary focuses on nonconformance/conformity. The distinction between conformity and conformance as internal vs external requirements is not formally defined by ISO itself. Instead, it’s more of an interpretation used in quality management discussions. External noncompliance refers to breaches of laws or regulations, which may involve nonconformities, but is a broader legal concept.
Nonconformity vs noncompliance vs deviation: are all deviations nonconformances?
Although often used interchangeably, these terms (Nonconformity vs noncompliance vs deviation) have distinct meanings:
- Nonconformance, or nonconformity: Failure to meet a defined requirement (internal or external).
- Deviation: A departure from an approved process or expected outcome, often temporary or unplanned.
- Noncompliance: A breach of external laws or regulations that may result in enforcement actions or penalties.
So, are all deviations nonconformances? In short, a deviation is a departure from an expected process or requirement. If not properly addressed, a deviation may result in a nonconformance, and a nonconformance may in turn lead to noncompliance, which may have potential regulatory consequences.
What are the different types of nonconformances?
There are three main types of nonconformances: minor, major, and critical nonconformities. Every company typically decides the criteria for defining the severity of a nonconformance based on its specific products, services, and processes.
It is important to note that the severity and the level of nonconformance may vary depending on the context, industry, risk level, and regulatory expectations.
What is a minor nonconformance in one industry can be considered a major in another.
What is a minor nonconformance?
Minor nonconformances do not significantly impact the quality and safety of the product or service and do not affect the reliability and integrity of the management system. Most minor nonconformities are often isolated cases that could be fixed easily.
What is a major nonconformance?
On the contrary, a major nonconformance is a failure to meet requirements that are likely to significantly impact the quality, safety, or compliance of the product or service. Major nonconformities may be repeated occurrences or complex problems that adversely affect production processes and products, and require great resources, effort, and time.
What is a critical nonconformity?
Critical nonconformities pose immediate and serious risks to patient safety or regulatory compliance. These typically demand urgent containment actions and management escalation.
Examples of minor, major, and critical nonconformities
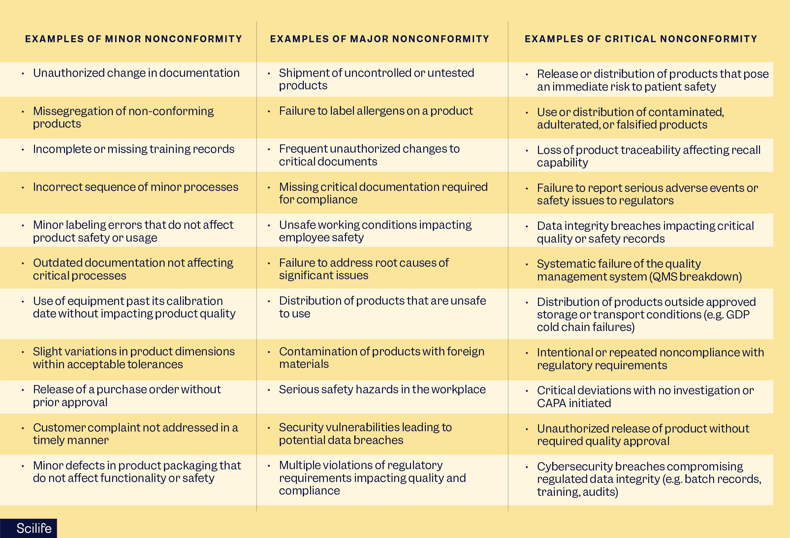
Please note that these lists are not exhaustive, and the order of presentation is random, with no implied priority.
Common nonconformances
In this part, we’ve listed the most common nonconformities for ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and highlighted the importance of maintaining rigorous quality management practices to ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
You should address these areas effectively to avoid costly nonconformances and improve your overall quality management system.

Why effective nonconformance management is critical
Effective nonconformance management in life sciences is critical because it protects patient safety, ensures regulatory compliance, and prevents small issues from escalating into serious quality or business risks.
By identifying, investigating, and correcting nonconformances in a structured way, organizations reduce the likelihood of repeat issues, audit findings, recalls, and operational disruptions.
When managed effectively, nonconformances become opportunities for continuous improvement rather than sources of risk and uncertainty, as well as a chance to strengthen processes and prevent recurrence when addressed systematically.
How to avoid nonconformances and minimize risk
Avoiding nonconformities or minimizing the risk of recurrent events before they grow is key to maintaining quality and compliance. Let’s learn some practical tips to prevent or minimize risks and ensure your business stays on track and runs smoothly:
1. Regular internal audits
Systematically checking your processes against ISO 9001, ISO 13485, or FDA 21 CFR 820 with a well-established internal audit plan allows you to observe your processes with a fresh pair of eyes and detect potential issues early. Moreover, Scilife takes the complexity out of your audit management by offering features that enable you to manage your internal audit without hassle.
2. Continuous employee training
Training your employees continuously allows your team to be aware of the latest procedures and regulations. Additionally, adding an effectiveness check step makes training sessions more engaging.
The Scilife Training tool offers you a more streamlined training management process with function-based training plans, automated training activities, and a dashboard where you can track the training-related metrics.
3. Risk management activities
Organizational risks should be assessed regularly, using quality tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). Proactively identify areas where nonconformances could occur and assess their impact to reduce the risk of those nonconformances happening by implementing controls before they become costly.
4. Establish effective CAPA processes
The CAPA process helps to correct and prevent any issues. Having a cloud-based QMS CAPA module helps you to manage your process systematically, including addressing nonconformities quickly, investigating and identifying the root cause(s), as well as implementing (Corrective and or Preventive) actions to prevent recurrence, and regularly reviewing the effectiveness of these actions.
5. Implement robust document control
A well-established document management system keeps operations running smoothly. Documents should clearly define processes to help eliminate misunderstandings and reduce the risk of errors, and the latest versions should be available to relevant employees within the organization to prevent outdated information.
Good documentation supports compliance and makes it easier to track and improve your processes. Additionally, all employees should know that when a change is needed, it should be made through documents and change control systems.
6. Supplier quality management
Regular evaluation and audit of suppliers helps you to ensure that they meet predefined quality standards. The Scilife Supplier module offers you integration within other QMS processes so you can select, evaluate, quality, monitor, audit your suppliers, execute Supplier NC reports, and keep all supplier files digitally in one place.
7. Measure nonconformance performance KPIs and metrics
Key metrics for monitoring nonconformance management include:
- Time to close NCRs
- Nonconformance recurrence rate
- Number of overdue NCRs
- CAPA effectiveness rate
- Nonconformances by site, process, or supplier
Tracking these KPIs will help you identify trends, allocate resources, and continuously improve quality performance.
8. Use quality management software
Leverage quality management software like Scilife to streamline processes and automate documentation. This can reduce manual errors and provide real-time data for better decision-making, but also enhance effectiveness and overall compliance.
What are the steps in nonconformance management?
To handle nonconformances effectively, teams should follow a clear, repeatable process that moves from identification to corrective action and ongoing monitoring. So, here are the steps in nonconformance management:
- Identification and detection: identify deviations through audits, inspections, complaints, or monitoring activities.
- Documentation: record details in a nonconformance report (NCR), including description, impact, and evidence.
- Containment and correction: implement immediate actions to limit impact and restore control.
- Root cause analysis: investigate underlying causes using structured methods.
- Corrective actions (CAPA): define and implement actions to prevent recurrence.
- Effectiveness check: verify that corrective actions are working as intended.
- Closure and monitoring: formally close the NCR and monitor for trends or recurrence.
Nonconformance report template
Equally as above, writing a structured, easy-to-follow, and effective nonconformance report is critical. Not only because it is a statutory requirement, but also because every non-conformance report is associated with certain risks and opportunities to be tackled.
One way to do it easier for yourself is using a nonconformance report template to help ensure consistent documentation, including:
- Description of the issue
- Corrections and corrective actions
- Approvals and responsibilities
In other words, nonconformance report templates help you reduce errors and support regulatory compliance, whilst documenting all necessary details regarding a nonconforming process or product.
The NCR template helps your organization to collect all the data that is required for ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and FDA, such as the NC description, correction(s), corrective actions (and preventative actions if any), and approvals ofthe NCR owner and Quality manager at a minimum of the personnel.
Scilife tips: how do you manage nonconformances in a QMS?
How do you manage nonconformances in a QMS? Scilife’s eQMS software offers automation and a streamlined process for nonconformance management in life sciences, and it makes the process more efficient and effective. The most common benefits of a well-designed eQMS with nonconformity management features are the following:
- Automated reminders, notifications,
- Predefined workflows
- Robust reporting tools
- Collect and analyze data efficiently
- Track corrective measures in real time
- Customizable non-conformance report templates
- Customizable workflows for approvals of each phase of NC
- Traceability of the NCR owner, task assignees, approvers, and timestamps of each action.
- Monitoring previous events with details such as their root causes, how they were handled, dispositioned, etc.
You cannot measure the cost of a nonconformance by summing up all resources used. It’s an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement; therefore, you should foster a quality culture where quality is everyone’s responsibility.
By integrating all these aspects, QMS software helps life sciences businesses maintain high and uniform quality, ensure compliance with requirements, and minimize the risks and costs associated with nonconformances.
Conclusion
Still wondering how to manage nonconformances in a QMS? Scilife is designed specifically for the needs of life science companies, offering powerful features to help you strengthen nonconformance management capabilities, improve both quality and compliance efforts, and increase efficiency. By providing integration between QMS processes and pre-defined workflows, users are guided through the phases of the nonconformance management process.
FAQs
Is every nonconformance a CAPA?
Not every nonconformance requires a CAPA. Minor, isolated nonconformances may be addressed through immediate correction if there is no significant risk and no evidence of recurrence. However, major, recurring, or high-risk nonconformances typically require a formal CAPA to identify root causes and prevent the issue from happening again.
Who owns a nonconformance?
Ownership of a nonconformance usually lies with the process owner responsible for the affected activity, while the quality team provides oversight and ensures regulatory expectations are met. Clear ownership is essential to ensure timely investigation, corrective action, and closure.
How long should a nonconformance remain open?
There is no fixed timeframe, as the duration depends on the severity, complexity, and risk of the nonconformance. That said, regulators expect nonconformances to be addressed and closed in a timely manner, with documented justification for any extended investigations or actions.
What happens if nonconformances are not closed?
If nonconformances are not adequately investigated, corrected, and closed, they can recur, escalate into major or critical issues, and lead to audit findings, regulatory action, product recalls, or risks to patient safety. Poor nonconformance management can also signal weaknesses in the quality management system.