Quality is paramount in the Life Sciences industry. After all, the safety and efficacy of its products can have a direct impact on patient health.
Therefore, implementing an effective and efficient Quality Management Systems (QMS) is not only essential for regulatory compliance but also gives you a leg up on gaining a competitive advantage over other market players.
For decades, the paper-based QMS was the standard for Life Sciences organizations. Using a paper-based system was easy to implement and simple to use. However, even the best paper QMS has its flaws. The risk of accidentally bypassing regulatory requirements poses a risk during inspections. And today, just having a paper-based system puts inspectors on high alert.
Current data Integrity regulations require a higher degree of compliance and control. The efficiency of a paper-based QMS is limited and cannot maintain those requirements over time.
When there is the need for compliance, scalability, and risk reduction, an electronic Quality Management System (eQMS) is the perfect fit.
In recent years, the shift towards eQMS software has gained significant momentum, revolutionizing how organizations manage their Quality processes.
The challenge here is to decide whether to stay with your old paper-based system or make the leap to a new eQMS. Once you decide to go digital, the next challenge is to decide on the right tool that will enable you to comply with regulations out of the box.
In this blog post, I will delve into the hidden costs associated with not having a robust eQMS solution, comparing it to manual systems and the widely-used but generic Microsoft SharePoint software. Brace yourself and get ready to uncover the untapped value that lies beyond mere Quality compliance!
Why Do We Need an eQMS in the Life Sciences?
The perceived “free” existence of paper can create the illusion of an easy and cost-effective solution. I understand it is tempting to remain paper-based. With a large stack of paper readily available in the office, it may seem logical to adopt it for managing your QMS processes. However, do not be deceived by this apparent advantage! There are hidden costs you should consider that could impact your business efficiency.
However, customizing generic tools like Microsoft SharePoint will not guarantee low expenses at no risk either.
Let’s find out why.
While paper-based systems may seem convenient at first, there are long-term consequences that could seriously jeopardize your organization’s success. The labor-intensiveness of managing a paper-based QMS can be like a relentless whirlpool, draining precious time and resources. Manual efforts consume valuable working hours, leaving your staff entangled in a web of document handling, futile searches, and endless battles to maintain compliance.
But don’t fret; there is a solution that will safeguard your organization’s excellence: eQMS software.
By adopting an eQMS, you can benefit from automated safeguards and seamless data integrity. This advanced system will ensure that your path to excellence remains intact, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: delivering the highest Quality products and services while staying compliant with regulations.
An eQMS has a set of processes to help you run a better, more efficient QMS that focuses on true Quality and protects patients as the recipients of your products.
Don’t be swayed by the illusion of paper’s simplicity or Microsoft SharePoint functionalities. Embrace the efficiency and reliability of eQMS software and take your Life Sciences organization to new heights of success. Experience the transformative power of technology and leave the inefficiencies of the past behind. Your journey to excellence begins with embracing the future.
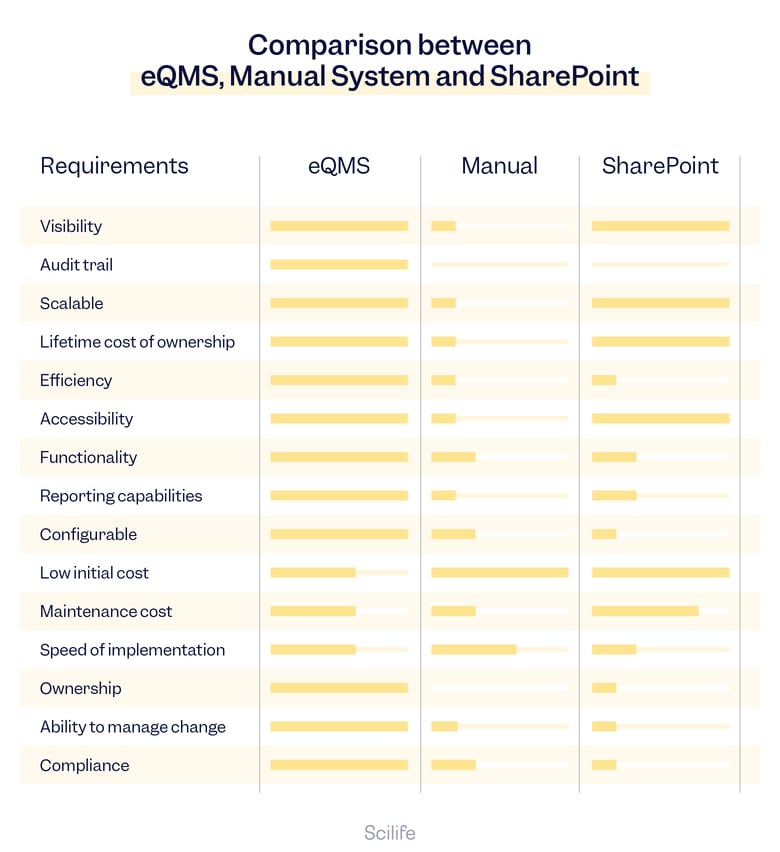
eQMS vs. Paper vs. SharePoint
Visibility
Visibility refers to the ability to have clear and comprehensive insight into the entire Quality process.
eQMS
An eQMS offers real-time visibility and clarity into Quality processes. Organizations can monitor compliance with industry regulations and standards. The system empowers users to track documents, approvals, and actions instantly, fostering seamless collaboration and facilitating well-informed decision-making throughout the organization.
Manual QMS
Visibility in manual systems relies heavily on inefficient manual reporting and communication, which may lead to delays, data inconsistencies, and lack of real-time insights. Gaining an accurate clear visibility of Quality processes might be challenging and time-consuming.
SharePoint
While SharePoint can provide visibility through document libraries and lists, it may not offer the same level of visibility as a dedicated eQMS solution, unless you make efforts to make an extensive customization. Data retrieval and reporting might not be as efficient with the basic package as with an eQMS solution.
Audit Trail
Audit trail refers to the ability of the system to track and record changes made to Quality management processes.
eQMS
eQMS excels in maintaining robust audit trails. Detailed logs of user actions, document changes, and system interactions are automatically recorded, ensuring compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 and EU GMP Annex 11 requirements for data integrity and accountability.
Manual QMS
Audit trails in manual systems heavily rely on manual record-keeping, which can be error-prone and difficult to manage, potentially leading to incomplete or inconsistent audit trail documentation.
SharePoint
To achieve a complete and compliant audit trail in SharePoint, it may require significant customization and additional third-party integrations.
Scalability
Scalability refers to the measure of a system’s ability or software to adapt to changes in application and system processing demands.
eQMS
eQMS are designed to scale with the growing needs of an organization. As the organization expands, eQMS can handle increasing amounts of data and users without significant disruptions or loss of performance.
Manual QMS
Manual systems can become cumbersome and inefficient as the organization grows. They may struggle to keep up with the increasing volume of documents and data.
SharePoint
SharePoint may be limited for advanced Quality management needs. Extensive customizations and infrastructure upgrades might be necessary to meet growing needs.
Lifetime Cost of Ownership
Lifetime cost of ownership refers to the total cost of owning and operating a QMS over its lifetime.
eQMS
While the initial investment in eQMS might be higher, the long-term cost of ownership is more economical. eQMS reduces the cost of maintaining paper-based systems, such as printing, storing, and retrieving documents. Streamlined processes, reduced human errors, and lower compliance risks lead to increased efficiency, productivity and cost savings over time.
Manual QMS
The initial implementation cost of a manual QMS may be lower than eQMS or SharePoint. However, this apparent lower initial cost hides the higher lifetime costs associated with manual labor, increased risk of non-compliance, and limited scalability.
SharePoint
SharePoint may seem to be a cost-effective solution initially compared to eQMS. SharePoint comes “free” with many Microsoft Office packages. However, if you want to use it to its full potential for Life Sciences, it is far from free. SharePoint has an expensive licensing structure, and hidden costs to implementation that might add up very quickly to the total cost of the project.
Efficiency
Efficiency in the context of Quality systems refers to the ability of the system to streamline and automate Quality management processes, thus reducing the time and effort required to complete basic tasks.
eQMS
eQMS offers enhanced efficiency through automation and streamlined workflows out-of-the-box, task assignments, and alerts. This reduces manual intervention, speeds up processes, and minimizes bottlenecks. eQMS is built and customized to overcome Quality objectives and minimize complexity. eQMS vendors usually provide assistance on how to utilize every module and ensure a shallow learning curve.
Manual QMS
Manual QMS are more time-consuming, relying on manual data entry and document handling, which may result in delays and inefficiencies.
SharePoint
SharePoint can improve efficiency to some extent with basic automation, but compared to eQMS, it may lack some advanced features required for a fully efficient QMS.
Accessibility
Accessibility refers to the ease of access to the system and its features.
eQMS
eQMS provide remote accessibility, allowing authorized users to access and contribute to Quality processes from anywhere, ensuring compliance, facilitating collaboration and real-time decision-making. It is easier to track and manage data, documents, and workflows.
Manual QMS
Accessibility relies on paper-based or spreadsheet-based processes that require manual effort for document control, data entry, and tracking. Accessibility is limited to physical locations, potentially hindering communication and response times between different sites.
SharePoint
SharePoint’s online capabilities enable remote access and easy accessibility to Quality processes, although it might require additional configurations and security considerations.
Functionality
Functionality refers to the features and capabilities of a system or software to perform specific Quality management tasks or processes.
eQMS
eQMS is a dedicated software system designed to manage and automate Quality processes, including document control, training management, audits, Quality events, CAPA management, change control, risk management, and KPI management. It provides comprehensive features and workflows specific to Quality management.
Manual QMS
Manual systems rely on paper-based or spreadsheet-based processes. They require manual effort for document control, data entry, and tracking, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
SharePoint
SharePoint is a web-based collaboration and document management platform that allows users to create, store, and share electronic records. While it can be used for basic document storage and collaboration, SharePoint is not fully compliant out-of-the-box with 21 CFR Part 11. Meet regulatory requirements requires additional customization and configuration, such as:
- Enforcing strong authentication and access controls.
- Implementing electronic signature functionality.
- Implementing audit trails to track who made the changes, when they were made, and what was changed.
- Ensuring that electronic records are accurate, complete, and legible, and that they can be easily retrieved and reproduced.
- Implementing controls to prevent unauthorized changes to electronic records.
Reporting Capabilities
Reporting capabilities refer to the ability of the system to generate reports and visualizations that provide insights into Quality management processes.
eQMS
eQMS offers advanced reporting capabilities, generating real-time insights into Quality metrics, and KPIs, that spotlight trends involving nonconformances, audits, complaints, and more. Dashboards provide real-time management of recorded data and timely closures of Quality tasks. Pre-built reports streamline decision-making and compliance reporting.
Manual QMS
Reporting in manual QMS requires manual data compilation and analysis, leading to delays and potential inaccuracies in compliance reporting. Real-time reports and visualizations are difficult and time-consuming to generate.
SharePoint
SharePoint provides basic reporting features, but it may not offer the same level of visualization and depth as dedicated eQMS solutions.
Configurability
Configurability refers to the ability of the system to be customized and adapted to fit the specific Quality needs and processes of an organization.
eQMS
eQMS are highly configurable to align with specific organizational needs and compliance requirements. Customization is achieved without extensive development and validation efforts made by developers and vendors. This allows users a smoother transition to digital capabilities, reducing unnecessary workload for teams.
Manual QMS
Manual systems have limited configurability, as they rely on paper-based or spreadsheet-based processes that are difficult to customize. Manual QMS potentially leads to process misalignment and compliance gaps.
SharePoint
SharePoint is configurable to some extent, but achieving full compliance and optimal alignment with Quality management processes might require significant customization and resources.
Initial Cost
Initial cost refers to the cost of implementing the system.
eQMS
The initial cost of implementing eQMS is higher due to software licensing, implementation, and training. However, the benefits in terms of efficiency and compliance often outweigh the upfront investment.
Manual QMS
The initial cost of manual systems might appear lower, but it might not cover the full scope of Quality management needs, leading to hidden costs and potential compliance risks.
SharePoint
SharePoint’s initial cost might seem appealing, but additional expenses for customizations and third-party integrations can significantly impact the overall investment.
Maintenance Cost
Maintenance cost refers to the cost of supporting and updating the system over time.
eQMS
Maintenance costs for eQMS primarily involve software updates, technical support, and hosted services. The cost is relatively predictable and manageable compared to manual systems.
Manual QMS
Manual system maintenance costs can be unpredictable and may include expenses for process improvement, training, printing, manual record-keeping, storing, and retrieving documents. They are higher than eQMS or SharePoint due to increased labor costs, inefficiencies, and potential compliance issues.
SharePoint
Maintenance costs for SharePoint are cost-effective initially, but can vary depending on the extent of customizations and integrations, potentially leading to higher long-term expenses.
Speed of Implementation
Speed of implementation refers to the time it takes to deploy the system within an organization.
eQMS
Implementing an eQMS can involve a certain amount of time and effort, as it requires configuring the system to fit the organization’s specific needs and processes, as well as meeting regulatory requirements. However, the implementation is more straightforward if the vendor provides supplementary onboarding service, like holding frequent meetings on the progress of the project to completion, data importing, training, and validation package.
Manual QMS
Manual eQMS tend to have a relatively faster implementation time than eQMS or SharePoint, as they often involve simple paper-based or spreadsheet-based processes that can be set up relatively quickly.
SharePoint
Even when properly configured, SharePoint may have a slower implementation time than a manual QMS or eQMS, as it will need more resources to customize the system according to regulatory requirements.
Ownership
Ownership refers to the responsibility of upkeeping the system over time.
eQMS
Organizations that opt for eQMS solutions have a clear ownership structure with dedicated personnel responsible for system management and compliance.
Manual QMS
Ownership of manual systems is less defined, leading to potential inefficiencies and difficulties in enforcing accountability.
SharePoint
SharePoint requires organizations to take on the responsibility of verifying that the system aligns with regulatory requirements concerning data ownership and the use of electronic signatures. This necessitates the allocation of additional resources and specialized knowledge to ensure full compliance. As a result, organizations using SharePoint as their QMS must dedicate effort to ensure that the platform meets the necessary standards and fulfills the stringent regulatory demands in the Quality-critical environment of the Life Sciences industry.
Ability to Manage Change
Ability to manage change refers to the system’s capability to ensure changes to Quality management processes are properly documented, reviewed, and approved before implementation.
eQMS
eQMS integrates existing tools and change management processes out-of-the-box, managing individual change requests according to applicable regulations.
Manual QMS
Manual systems may have a weak change control procedure, making it difficult to manage changes effectively with paper-based processes.
SharePoint
SharePoint can drive change requests only with customized applications based on the latest GxP requirements. However, the basic package does not provide the same level of functionality and scalability as a dedicated eQMS.
Compliance
Compliance refers to adhering to the rules, regulations, and standards set by regulatory bodies and industry associations to ensure the safety, efficacy, and Quality of products and services.
eQMS
When it comes to compliance, eQMS offers distinct advantages. A well-designed eQMS is specifically tailored to meet the stringent requirements of the Life Sciences industry. It comes equipped with built-in features and functionalities designed to facilitate compliance with various regulatory standards, such as FDA regulations, EU GMP Annex 11, and 21 CFR Part 11. Here, eQMS solutions include robust audit trails, electronic signatures, and automated workflows, which are critical for maintaining data integrity and ensuring the traceability of Quality processes. Additionally, eQMS platforms continually update their systems to stay current with the evolving regulatory landscape, sparing organizations the burden of constantly monitoring and adjusting their systems.
Manual QMS
Compliance with manual systems can be challenging and prone to human errors. Manual processes lack the built-in safeguards and automation that eQMS offers. Document control, versioning, and maintaining an accurate audit trail can be cumbersome in manual systems, potentially leading to compliance gaps and data integrity issues. Manual systems require rigorous training, monitoring, and ongoing vigilance to ensure that all employees adhere strictly to established procedures, which can be resource-intensive and error-prone.
SharePoint
SharePoint can drive change requests only with customized applications based on the latest GxP requirements. However, the basic package does not According to the Microsoft 365 GxP Guidelines, the responsibility for meeting data integrity principles (ALCOA) is “shared between Microsoft and GxP regulated customers. While Microsoft offers a secure and compliant platform for services, applications, and data, the customer bears the responsibility for authorizing access, managing data governance, and configuring settings related to data integrity.”
The customers’ responsibilities are:
- Authorize users to access select resources.
- Configure and monitor the Microsoft 365 audit log.
- Enable library versioning settings.
- Define data classification and retention rules.
- Configure information rights management.
- Enforce desired level of encryption for network session.
- Establish proper controls over the use of system IDs and passwords.
- Manage user password authentication mechanism.
- Manage anonymous access and external sharing.
- Secure the software and hardware used to access Microsoft 365.
- Conduct end-user training.
As you can see, SharePoint is highly configurable. However, SharePoint does not have a built-in electronic signature approval solution to comply with Eu GMP Annex 11 and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 regulations on digital signatures functionality. You will need third-party integrations and your own development resources to achieve some of these most demanding FDA requirements.
Do you have the budget, time, knowledge, expertise, and patience to build a QMS from scratch using SharePoint according to current regulatory requirements? Doing it yourself will be quite challenging.
Final Words
When evaluating QMS options today, the eQMS emerges as the most reliable choice for the Life Sciences. Its purpose-built features, automated workflows, and adherence to regulatory standards make it a robust solution for organizations in this highly regulated industry as they are aiming to maintain regulatory compliance, data integrity, and the highest Quality standards. Manual systems, while feasible, are more susceptible to errors and resource-intensive. Microsoft SharePoint, although configurable, will require additional effort and third-party integrations to meet stringent regulatory requirements, making it a less optimal choice for Life Sciences organizations seeking a comprehensive compliance solution for their Quality management processes.
Discover how Scilife Smart eQMS can help you avoid extra costs and compliance failure!






