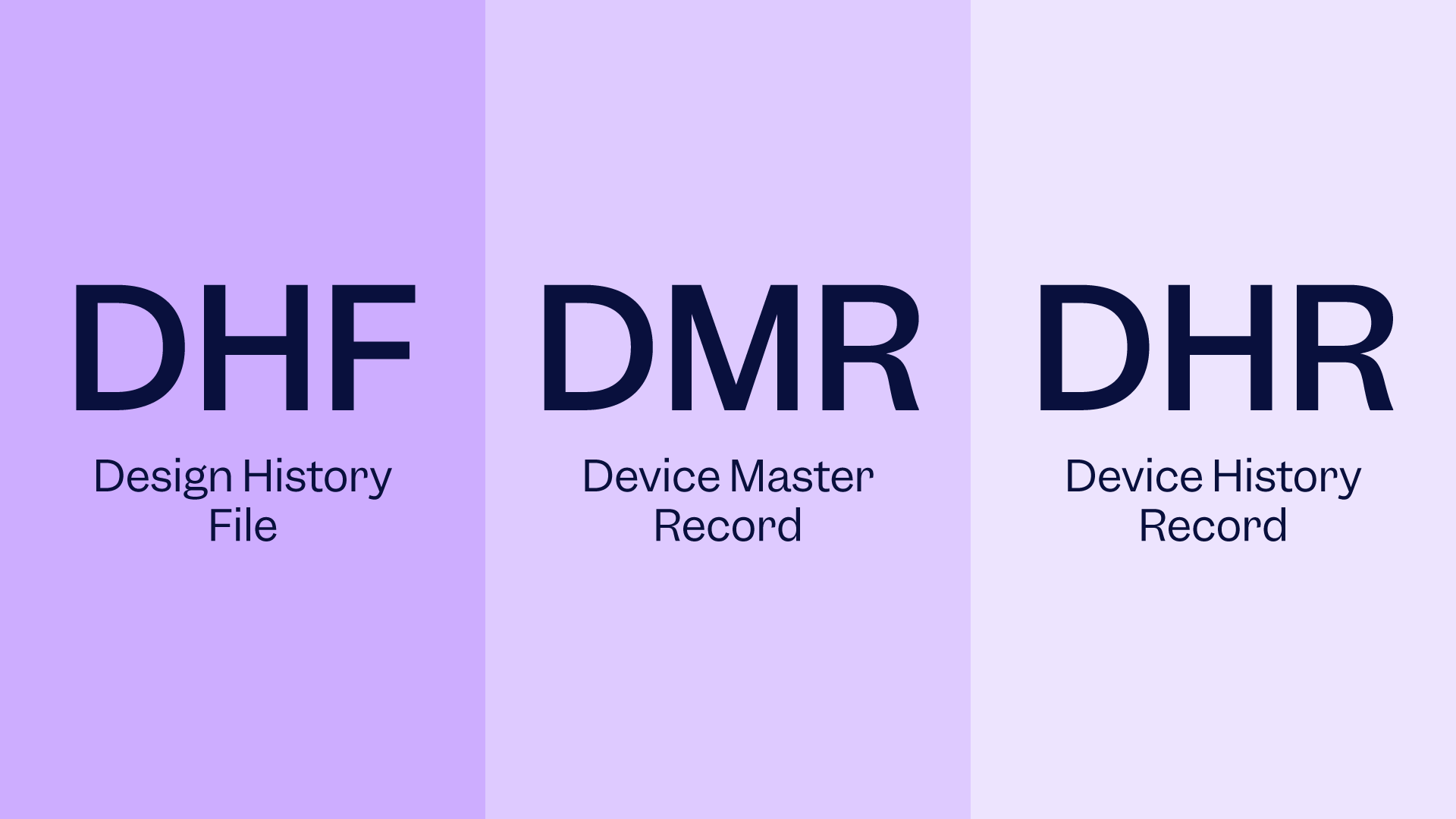
Managing your documents doesn’t have to feel like a never-ending nightmare. Good documentation practices, also known as GDocP, are essential to streamlining your document workflow, enhancing employee efficiency, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Let’s take a closer look into how good document practices will not only revolutionize your document management approach but keep your auditors smiling too!
The Trouble with Tradition: Are You Clinging to the Past?
Sometimes managing documentation can be challenging in today’s rapidly changing world. From lost files, to slow approval processes, traditional paper-based solutions create barriers to productivity and compliance. You’ll be one step closer to finding a better solution that works by identifying these challenges.
1. Paper-based vs. electronic QMS: A No-Brainer
In the pursuit of continuous improvement, a paper-based Quality Management System (QMS) often creates more issues than it solves in today’s business environment. Any alteration, big or small, consumes more time than is acceptable. Additionally, the storage space required for paper-based systems is both unsustainable and chaotic. So, transitioning to an electronic QMS (often also referred to as eQMS) isn’t just smart—it’s unavoidable. This shift makes it easier to manage Quality effectively and efficiently while reducing your carbon footprint. It also aligns with GDocP. All those benefits make the eQMS a wise investment.
2. Defining the Quality Records Management Hierarchy
Understanding the QMS pyramid model is pivotal before you define a hierarchical documentation structure within your QMS.
A well-planned QMS resembles a pyramid, five different levels interplay, with the Quality policy as its pinnacle. Underneath, you’ll find different layers such as Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and various protocols. Understanding how these layers interact is key to developing a system where documents flow seamlessly.
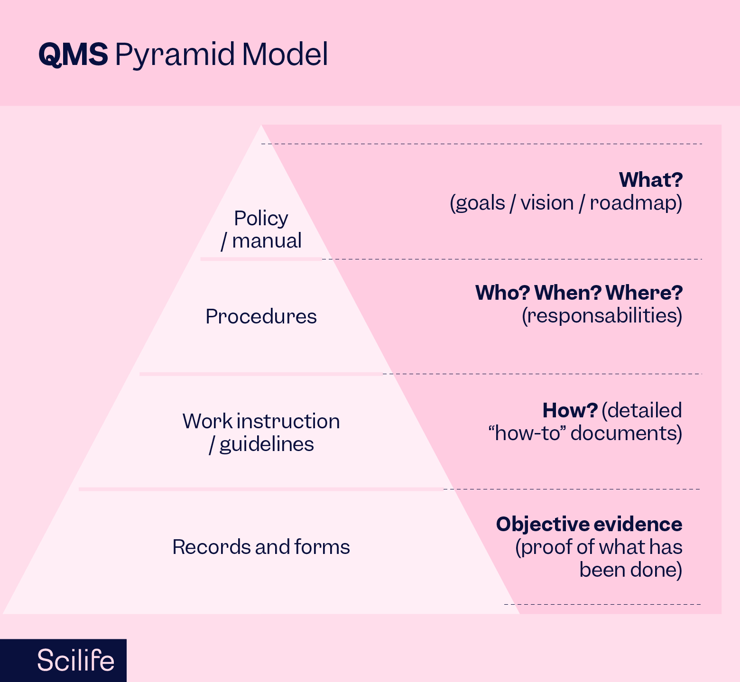
This hierarchy allows for the intricate linking of documents as either parent or child documents, each playing a specific role within the system. SOPs, for instance, can be master documents containing relevant workflow instructions, embodying the essence of good document practice.
For further information check out this short course:
3. Defining Applicable QMS Standards
Selecting the right standards and regulations before starting the implementation of a QMS is a key step in aligning with industry-specific requirements. Stay ahead by keeping up-to-date with FDA and ISO regulations relevant to the Life Sciences. Knowing what’s expected will ensure you’re compliant, so you can focus on achieving your business goals. You might consider the latest FDA and ISO regulations such as:
FDA 21 CFR:
-
- Part 11: Electronic records and electronic signatures
- Part 211: Drug and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Part 820: Medical device manufacturing and distribution
ISO:
Medical Device Regulations:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GMP
4. Defining the Records Management Workflow
Traditional manual processes for handling documents (for example, the use of email or handing out printed documents) can lead to delays, loss of information, miscommunication, or even missed deadlines. GDocP advocates for a built-in workflow within the document management system.
A well-designed eQMS includes an intuitive workflow that defines key processes such as drafting, reviewing, approving, distributing, accessing, storing, updating, and retaining documents and a heck of a lot more. The workflow built right into the document management system lets employees send documents (e.g., SOPs, deviations, CAPAs) to the right people with the click of a button.
During the definition step of an electronic document management process, a clear definition of the main workflows is essential. Here are some important questions to ask to ensure good document practice:
- Who will draft the documents?
- Who will review the different types of documents?
- Who will have the final authority to approve the documents?
- How will the documents be distributed?
- Who will have access to each type of document?
- How long will the documents be retained?
- How often will the documents be updated?
- How long is the substituted document retention period?
Implementing an eQMS is an opportunity to streamline these processes and simplify or discard manual tasks that don’t add value.
5. Electronic Signatures: Your New Best Buddy at Work
Electronic signatures are modern-day marvels in the world of GDocP, so forget pen and paper! They minimize the risk of unauthorized changes, forgeries, or undersigning, ensuring that documents remain secure and legally binding.
Their application meets current security requirements and protects businesses from potential legal or compliance pitfalls, making them an essential component of contemporary documentation management.
Further reading: Choosing a 21 CFR Part 11 compliant QMS
6. Cloud-Based Systems: The Sky’s the Limit
Migrating to a cloud-based QMS is another significant step towards aligning with GDocP. The cloud-based system offers scalability, real-time collaboration, universal accessibility, and adds a layer of protection against data loss through standalone hardware failure, which makes it a preferred option for businesses today.
Additionally, there are unquestionable savings on infrastructure and maintenance, so it’s a win-win! By moving to the cloud, businesses can save up to 40%, providing both economic and functional benefits.
7. User-Friendliness: The Cherry on Top
Last but not least, organizations will have higher employee satisfaction when they use user-friendly, attractive, and effective digital tools. The transition from paper to electronic must be smooth and engaging, encouraging your team to embrace this change. A system that’s easy to navigate promotes a culture of efficiency and accountability.
Next, let’s look at how easily an eQMS can integrate into your existing operations for document management, events, CAPAs, training, risk assessments, audits, and more. When making a change from paper to electronic, you must encourage the entire team to buy in and create efficiency in the document management process.
Bonus: Roadmap to Transitioning to an eQMS
Assessment: Evaluate current processes and identify areas for improvement.
Selection: Choose the right eQMS that aligns with your needs.
Implementation: Plan and execute the transition with clear timelines.
Training: Educate your team to ensure smooth adoption.
Review: Continuously monitor and refine the system for ongoing success.
What’s Next on Your Checklist?
Good document practice is not just about ticking boxes for compliance; it’s an intricate part of your company’s backbone. Mastering these seven strategies will help you forge a path that’s efficient, secure, and you can transcend traditional barriers and cultivate a documentation ecosystem that is robust, flexible, and aligned with modern-day needs.
Learn how effortlessly an eQMS can integrate into your existing operations for document management, events, CAPAs, training, risk assessments, audits, and more. Embrace these good documentat practices and take the first step towards a more agile, responsive, and compliant future for your organization.
FAQs
What Are Good Documentation Practices (GDocP)?
Generally, GDocP govern the creation, maintenance, modification, and archival of documents. By ensuring that documents are accurate, clear, and consistent, they facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and increase business efficiency.
Why Are eQMS “Better” than Paper-Based Systems?
eQMS are preferred due to their efficiency, accessibility, security, and sustainability. Unlike paper-based systems, they allow real-time collaboration, easy updates, automated workflows, and are more environmentally friendly. As a result, they assist in the compliance with standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 13485.
How Do Electronic Signatures Work? Are They Legally Binding?
Electronic signatures are digital representations of handwritten signatures. encryption techniques are used to verify the identity of the signer and the integrity of the document. In most jurisdictions, electronic signatures are legally binding provided they comply with applicable laws such as the ESIGN Act in the US or eIDAS in the EU.
What Are the Key Benefits of a Cloud-Based QMS?
Cloud-based QMS offers advantages like real-time collaboration, scalability, cost-efficiency, automatic backups, and remote accessibility. These systems allow seamless integration across different platforms and provide additional protection against data loss.
How Do You Define the Records Management Workflow?
The records management workflow is a systematic process involving the creation, review, approval, distribution, storage, and disposal of documents. The document management process defines roles and responsibilities at every stage, ensuring compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
How Do You Ensure User-Friendliness in an eQMS?
Ensuring user-friendliness involves selecting an eQMS with an intuitive interface, providing adequate training, offering user support, and encouraging feedback for continuous improvement. The goal is to enable users to navigate and perform tasks easily, thereby promoting adoption and satisfaction.
What Standards and Regulations Must Be Considered in Good Documentation Practices?
Standards and regulations vary by industry and region. Common examples include ISO 9001, ISO 13485, FDA’s 21 CFR Part 11, GDPR, and GxP. It’s important to identify and understand the standards and regulations that are applicable to your business to ensure full compliance.
How Do You Transition from a Paper-Based to an eQMS?
Transitioning involves assessing current processes, selecting the right eQMS, planning and implementing the transition, training staff, and continuously monitoring and refining the system. Collaboration with stakeholders, clear communication, and proper change management practices are crucial for success.
How Long Should a QMS Retain Documents?
Document retention periods vary by document type, regulatory requirements, and business needs. A well-defined records retention policy that is aligned with applicable laws and standards must govern the retention and eventual disposal of documents.
What Is the Role of Electronic Signatures in Regulatory Compliance?
Electronic signature ensures the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of documents. Aligning with regulatory requirements such as 21 CFR Part 11, which governs electronic records and electronic signatures, ensures they facilitate secure and traceable signing processes.
Discover how Scilife Smart QMS can simplify the Document Control Process!