Over the past few years, the life science industry has undergone meaningful growth and change. So what should you expect in 2023? The pharmaceutical and med-tech industries have adapted, innovated, and are expected to undergo a sea of change in the years to come. Here are 5 trends within the Life Sciences as we see them at Scilife…
1. Artificial intelligence (AI)
Applied artificial intelligence (AI) offers a myriad of opportunities that could shift the paradigms of the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. Artificial intelligence uses learned machine intelligence to make predictions and execute learned actions. It is commonly used in many industries, including pharma, biotech, and healthcare. For example, pharmaceutical companies use AI technologies to streamline the drug discovery process, accelerate the research and development of drugs, create more affordable medicines and therapies, as well as reduce costs.
Additionally, AI can help pharmaceutical companies increase productivity, improve efficiency, and quickly produce life-saving drugs. Biotech companies have implemented AI technologies that have applications for the research and development of drugs and diagnostics, such as technologies that can identify biomarkers. Also, diagnostic devices use AI algorithms for image classification, which helps physicians diagnose diseases such as cancer. Other applications of AI in biotech include phenotype screening and microbiome analysis.
AI can also have a profound impact on the delivery of healthcare, particularly in several ways. As a result, AI can improve healthcare productivity and efficiency by handling repetitive and administrative tasks, thereby improving the day-to-day life of healthcare professionals by making their jobs easier. In the long run, practitioners who have more time to look after their patients will be able to maintain a higher level of morale and retain more patients.
As well as providing the means for life sciences organizations to engage with their patients and healthcare professionals in a more authentic and personalized way, AI can also assist them in doing so. When used in tandem with human teams, artificial intelligence can gain insights from massive data sets more quickly, processing data more efficiently - automating workflows to make business processes run more efficiently, and converting insights into actions to help businesses achieve more outstanding results.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the Global AI in Healthcare Market will be worth USD 164.10 billion by 2029; the market is expected to grow by 42.4% between 2022 and 2029; Robot-Assisted Surgery to dominate due to technological advancements. The market stood at USD 13.82 billion in 2022.
Medical technologies, such as diagnostics and robotic-assisted surgery, are a significant growth factor. Advanced computing and connectivity can be effectively integrated into healthcare and life science products so that those who can accomplish these tasks will have a great opportunity.
If you implement or plan to implement AI technologies, it is worth considering cybersecurity risks for the medical device industry. In addition, it is a good idea to work with partners who understand and are proactively prepared for the cybersecurity requirements of today’s medical device industry.
2. Digitalization to catalyze change in health
Virtual healthcare
People use health technologies in the comfort of their homes, which opens new doors for virtual healthcare. Virtual health devices can vary from essential wearable technologies to specialized health technologies that are CE-certified.
Telemedicine and telehealth
The journey accelerated after the pandemic. Most people avoid seeing a physician if their illness is not urgent. This is especially true for the elderly and people with acute or chronic diseases; they need to see a physician more frequently. So, telemedicine allows us to be consulted by physicians without taking contamination risks. Physicians can use sensors to track vital signs, health records, and other personal information and diagnose their patients through remote patient monitoring (RPM). A connected or manual device allows patients to track vitals online from home, and the data is added to a central database (i.e., the EMR).
Hybrid models offer more consumer-facing solutions, including face-to-face medicine and telemedicine. Finding the best way to use telemedicine presents challenges, but more virtual options are likely to appear. As telemedicine, virtual healthcare, and devices can store personal health data, keep in mind the risks and requirements of cybersecurity when producing and marketing such tools.
Furthermore, this data is sensitive, so specialized and educated people can only read it.
Wearable technology
The devices with wearable technology are marketed to and used by physicians to monitor patient health and track changes, such as fluctuations in blood pressure, heart rate, etc.
Furthermore, these devices have special features, such as oxygen sensors, or detect diseases, such as coronavirus, a day before symptoms appear.
It is estimated that more than 40% of people who wear smartwatches share the biometric information collected by the devices with their doctors. Most doctors believe that healthcare apps can be used to enhance the health of their patients, with 93% believing that health tracking technology will make their care decisions more straightforward. In addition, life science organizations can use the same biometric data in clinical trials to update medical teams on health statuses in real-time.
The technology available in the field of wearables is still limited to measuring parameters such as heart rate or blood pressure. However, despite the system's limitations, experts believe they will be overcome in the not-so-distant future. In fact, it is predicted that wearable technology will be able to support the diagnosis of certain diseases through the collection of data by 2023.
You may have heard of the term "Internet of Things (IoT)," which has been increasingly used in recent years. Correlatively, "The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)" has been increasingly used in the healthcare industry. IoMT allows us to monitor and track health remotely. As these devices are used for medical purposes, manufacturers should consider using the software as a medical device (SaMD) and the feasibility and security of having IoMT. The FDA's and EU MDR’s recognition of these devices and technologies as "medical" demonstrates the upward trend for the industry.
Wearable devices have grown exponentially in the past few years and are now worth over $10 billion. By 2023, the wearable medical device market is predicted to reach $27 billion. The most known Wearable Drugs and Wearable Devices are as follows:
- Activity Monitors
- Patches
- Smartwatches
- Smart Clothing
- Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Devices
- On-body Injector
- Handheld Injector
- Needle-Free Injector
- Wearable Injectors
- At-Home Self-Care
Interest in “beyond-the-pill” treatment approaches
There is increasing interest in wearable technologies, digital pills, and even gamification for disease prevention and treatment. For instance, VR is promising for distracting a person facing chronic pain. Meanwhile, personalized therapies will be increasingly preferred, and companies will receive tremendous momentum for developing digitally driven treatment solutions.
E-pharmacy
Within the last few years, the healthcare industry has had to find a solution for making their products available to patients. As a result, pharmacies have evolved through pandemics owing to many reasons.
- E-pharmacies are vital for patients who continuously need life-saving drugs.
- Tech-driven pharmacy delivery is making e-pharmacies advocates for chronic disease management.
- They can work nonstop to provide every kind of medicine and healthcare at any time. For those reasons, there will be an upward trend in e-pharmacies worldwide.
Cloud technology and Cloud-based management systems
Sometimes, you might notice that you are using cloud technology. It is used in many industries and provides a protected and cost-efficient environment for leveraging analytics. For example, life science companies rely on the security and centralized accessibility of the cloud. The cloud maintains thousands of records, and companies can access them from anywhere at any time. In the life sciences, physicians can use it to collect big sensitive data from hospitals or clinical trials and evaluate analytics.
Digital processes have been used for a long time and will increase in 2023. Paper-based processes are transformed into digital approaches to improve operational efficiency. In addition, digital processes are beneficial for driving regulatory compliance, allowing pharmaceutical companies to value this transformation to digital, as it provides cross-departmental data transparency.
Life science industries, such as pharma, medical device, and biotech, improve their processes to increase productivity, increase efficiency, and comply with regulations and requirements. Enterprises with fast-changing environments need to digitalize their operations. Digital training is a simple-but-crucial step.
Digital management tasks, such as online training, documentation, and e-signatures, make operations faster, trackable, foolproof, and secure. Digital management systems, especially online training modules, are cost-efficient. They can be accessed from anywhere and are personalized to each user. As a result, digital management technologies will continue to grow in 2023.
3. Research and development
Data science in drug discovery and development
In 2021, data science became a primary tool for drug discovery and development in the pharmaceutical industry. Therefore, data scientists need devices that can quickly and easily plug into existing workflows without implementing enterprise solutions. That way, companies will take advantage of opportunities while waiting to develop enterprise solutions.
Increased focus on research and development
To fulfill the needs of patients, life science companies are reevaluating their approach to research and development. For example, pharmaceutical companies use innovative technologies, such as machine learning and open-source software, crowdsourcing, innovation centers, and public-private partnerships to reduce the massive cost of research and development.
Innovative technology has advanced drug development and research. Traditionally, drug development and research fronted challenges by obtaining enough participants for clinical trials, which can take years. Technology has given drug manufacturers more control over clinical trials. Now, they can lower costs by recruiting fewer in-person participants. Digitalization of clinical trials allows biotech companies to integrate genetics with biometrics to determine underlying causes of conditions. Machine learning offers tremendous possibilities for drug research and diagnosing and treating patients.
The irruption of Smart Quality
The fast-changing Life Sciences Industry will bring new challenges to Quality Professionals, who will need to find new approaches to answer authorities and final customers' demands. The traditional compliance-only vision won’t be enough. Organizations, apart from transitioning from paper-based to digital systems, will be required to go a step further and think of Quality as a catalyst to create added value, instead of seeing it just as a cost of doing business. Here’s where Smart Quality comes into action.
Smart Quality is a new way of using digital tools within a digital transformation scenario; from doing digital to being digital. And how can organizations make that switch? Starting by implementing a Smart Quality platform that combines advanced analytics, personalized continuous learning, and gamification methodologies. By implementing this unique approach, employees across the organization have the opportunity and resources to take ownership of quality, going beyond the Quality department.
And what will the results be? Organizations that manage to implement a Smart Quality approach will achieve an overall improvement in company operations, performance, and innovation. Quality management will be visible and present in each and every step of the processes. Smart Quality will remove outdated manual manufacturing steps, improving accuracy, saving effort, and therefore cutting costs. The new data mindset will also enable more informed decision-making, reducing Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPAs). And, finally, it will also boost employee satisfaction allowing continuous learning paths adapted to the industry and organizational real requirements.
Discover how a Smart Quality Management Software can help you go beyond the compliance-only mindset!
4. Personalized medicine
Historically, drugs and medicine have been developed and marketed on a “one-size-fits-all” logic. Clinical trials were used to establish the most beneficial formulation for the broadest community. Currently, modern genomics allows us to tailor formulation to an individual based on their DNA. By knowing a DNA's role in our health and the body's ability to fight disease, we can predict where illness will occur, accurately diagnose diseases, and develop customized treatments. Personalized medicine reduces time and costs by identifying medical issues at their source: the patient's molecular and genetic profile. By analyzing a patient's genetics, medical professionals can identify risks. Personalized medicine also uses data collected from clinical trials, enabling physicians to create customized therapies and treatment regimens for each patient.
Precision medicine has the potential to solve issues by using patient information to refine drug development. For example, biomarkers are used to identify tumors and develop tumor-specific drugs. This precision medicine aims to solve the issue with the highest level of effectiveness and positive outcome for the patient. However, precision medicine manufacturing has challenges requiring more undersized, more specialized facilities. Despite these challenges, precision medicine has an upward trend in the pharmaceutical industry.
It is predicted that by 2025, most hospitals will be able to offer personalized medicine to their patients. In this way, doctors can identify patient groups based on their genetic makeup and prescribe medications based on that information. As more people gain access to their genome sequences over the next few years, this trend is expected to accelerate by 2027.
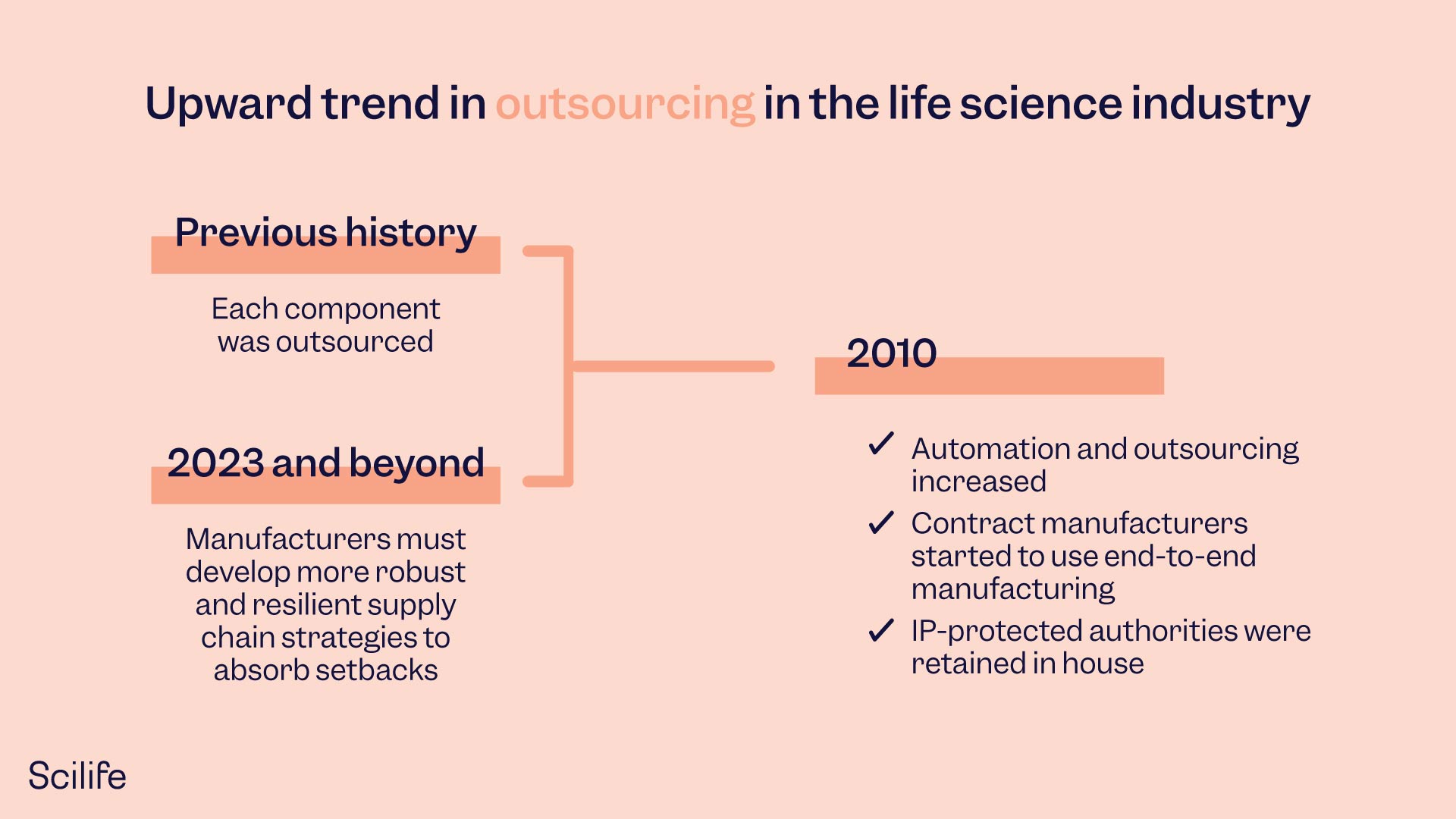
5. Supply chain strategy
Contract manufacturers experienced hardships during the pandemic, such as travel restrictions, transport delays, decreased production, and transport capacity limitations. Because of these hardships, freight prices are drastically increased. As a result, manufacturers must develop more robust and resilient supply chain strategies to absorb these setbacks. And supply chain resilience has become one of the top selection criteria for original equipment manufacturers. A resilient supply chain and contract manufacturer can confidently handle changing demands.
The bottom line
In 2023, Life Sciences trends will continue to create new opportunities as the digital industry evolves and leads innovation. And the innovations of today will have a significant impact on the medicine of the future. As we see it at Scilife, 5 trends to look out for are: the use of AI, digitalization as a catalyst for health change, research, and development, personalization, and supply chain strategy.
The pandemic accelerated rapid change in the life sciences trends, and the velocity will likely be maintained in 2023. The companies which adopt innovation and switch to digital for their products and operations (from discovery to clinical trials to treatment approaches) will be the ones that survive in such a competitive market.