A quality audit is an inseparable part of the life sciences business. This is because healthcare products can have desired as well as undesired effects on patients. Therefore, it is important to manufacture them by following the best practices in the industry. These best practices help to maximize therapeutic effects while minimizing the side effects.
The best practices in the life sciences industry are set out in the form of regulations by the world’s leading regulatory agencies and healthcare organizations. The purpose of these regulations is to protect the interest of the general public. Regulatory agencies and healthcare organizations perform quality audits of life science companies to monitor compliance with regulations.
Any adverse finding during an audit may cause severe legal implications and damage to the reputation of the concerned life science company. That is why life science companies must stay audit-ready all the time.
If you are also looking for ways to prepare your organization to be audit-ready, then this article is for you. Keep reading to learn the meaning of a quality audit, the types of quality audits, and some tips to prepare for a quality audit. Let’s begin by understanding the meaning of quality audit.
What is a Quality Assurance Audit?
A quality assurance audit is a systematic, and unbiased examination of an organization’s quality management system. The person who conducts the examination is known as the auditor. For examination, the auditor objectively reviews evidence relating to the company’s quality management practices and leaves behind an audit report. The audit report consists of the auditor’s findings during the audit. The auditor may also include concluding remarks regarding the company's quality management practices in the audit report.
After the audit, the company uses findings from the audit to plan corrective and preventive actions to improve compliance with the regulations. After improving compliance to the satisfaction of the auditor, the company may get a license or certification depending on the nature of the audit.
Quality audits can be internal audits or external audits depending on the auditor. Keep reading to understand the difference between the two.
Internal Quality Audit
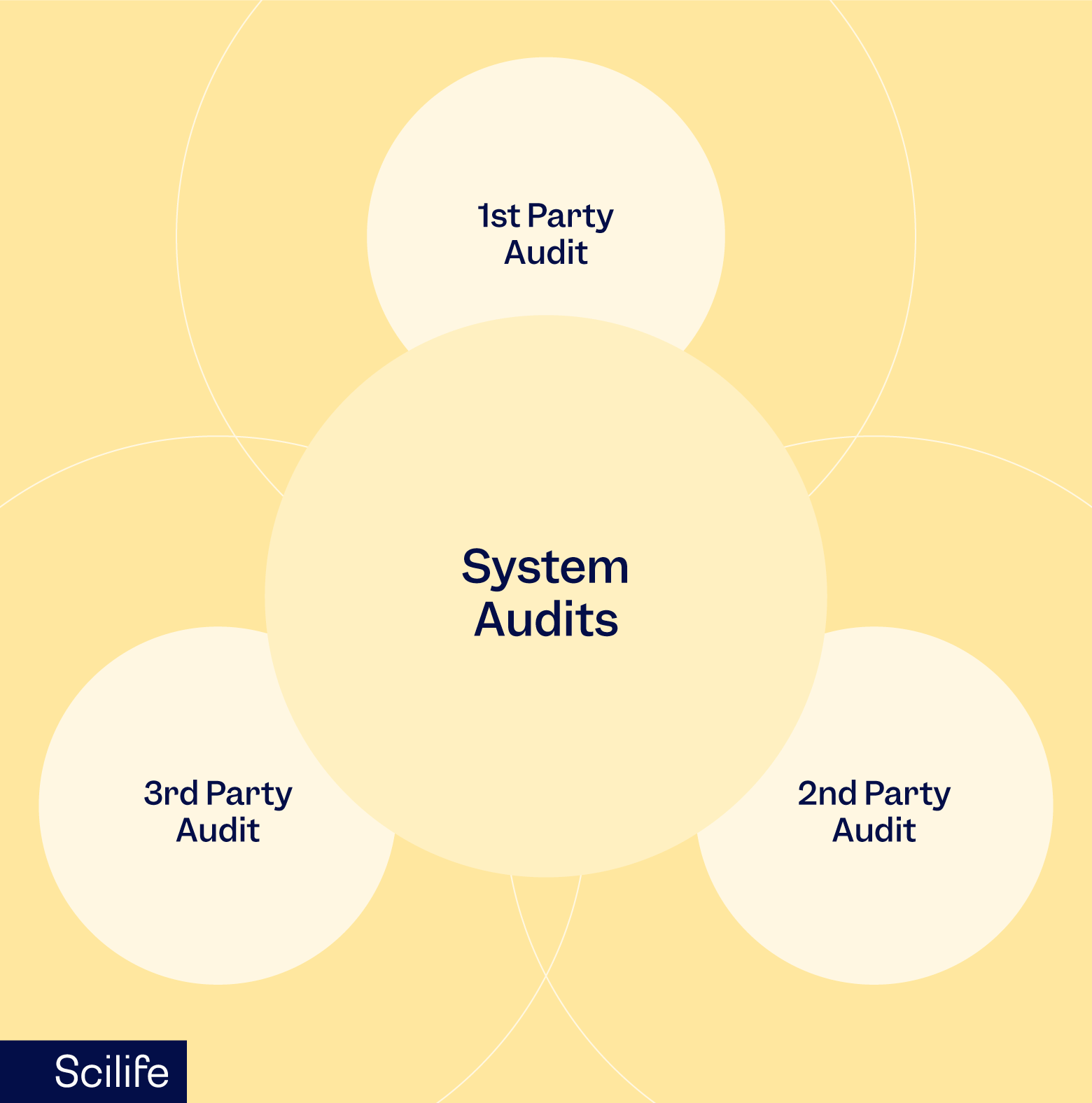
As the name suggests companies conduct internal quality audits by allocating the responsibility for auditing to an internal resource. As no external parties are involved in this kind of audit, an internal audit is also known as a first-party audit. The purpose of internal audits is to prepare the organization for the upcoming external audit by doing a mock audit.
Agencies such as the US FDA, ISO, and EMA recommend internal audits to strengthen an organization’s quality management practice. In case of adverse observations in an internal audit, you have nothing to lose. Every observation is an opportunity to avoid potential compliance issues in the future.
External Quality Audit
Unlike an internal audit, an external quality audit is conducted by an auditor who is outside the organization. An external quality audit can be either a second-party audit or a third-party audit.
Second-party Audit
A second-party audit is an audit in which the stakeholders are associated with you in the form of a supplier, customer, or contract manufacturer. Therefore, these audits can impact critical business decisions for your organization. An adverse observation in a second-party audit can cost you the termination of the manufacturing or a procurement contract. Hence, it is more crucial than an internal audit.
Third-party Audit
Third-party audits are conducted by auditors who do not have any conflict of interest or vested interest in your organization’s success as the auditors are appointed by the concerned regulatory agencies.
A third-party audit is the most crucial audit for any life science company as it may result in a certification or a license. An example of a third-party audit would be an audit in which a US FDA drug inspector visits your manufacturing site to confirm your organization’s ability to meet safety and efficacy standards as per US FDA requirements. Upon successful completion, you may get a license to manufacture and export the products to the USA.
An adverse observation in a third-party quality audit can cost you a warning letter, penalty, fine, or an injunction depending on the severity of the observation.
Types of system audits:
Some of the agencies that conduct third-party audits frequently are as follows:
US FDA Audit
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) conducts audits to ensure compliance with USA’s federal regulations and guidelines.
EMEA Audit
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is a regulatory body that evaluates and monitors the safety and efficacy of medicinal products for human and veterinary use within the European Union (EU).
MHRA Audit
The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is the UK's regulatory authority that ensures medicines and medical devices marketed in the United Kingdom meet the required standards of safety, quality, and efficacy.
WHO Audit
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. As the name suggests WHO monitors healthcare product safety, efficacy, and quality with a worldwide view without limiting its outlook to one specific country or a region. It provides leadership and coordination on global health matters, including disease outbreaks, health emergencies, and health systems strengthening.
BRICS Audit
BRICS is an acronym for Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. It is an association of emerging economies that work together to promote economic growth, reduce poverty, and enhance regional cooperation within the BRICS region.
ICH Audit
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is a global organization. As the name suggests ICH harmonizes requirements under different regulatory landscapes for ease of compliance.
ISO Audit
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is a non-governmental organization that develops and publishes international standards for various industries, including healthcare. Complying with ISO standards helps to boost employee confidence in meeting the quality, safety, and efficiency of healthcare products and services as per regulatory requirements.
EU MDR Audit
The European Union Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) is a regulatory framework that sets out the requirements for medical devices marketed in the EU region. It aims to ensure patient safety and improve transparency and traceability of medical devices.
Types of Quality Assurance Audits
Apart from the auditor, the purpose of quality audit also differentiates different types of quality assurance audits. Broadly quality audits fall into one of the following categories:
System Quality Audit
A system quality audit focuses on evaluating the conformance to the management system. These systems may include systems such as quality management systems or performance management systems. The purpose of any management system is a standardization of the workflow for the smooth operation of the business functions within organizations. Therefore, during a system audit, the auditor may cross-examine the actual workflow against the documented workflow.
Process Quality Audit
A process quality audit focuses on conformance to the established manufacturing process. The auditor evaluates the operating range of process parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, etc. The process parameters should be within acceptable range as per the regulatory filing data. Additionally, the auditor may verify if the in-process quality checks are being followed. Lastly, the auditor may also scrutinize the standard operating procedures, work instructions, flow charts, competence of personnel, and process specifications for conforming the adherence.
Product Quality Audit
A product quality audit focuses on conformance to the product quality standards such as visual appearance, shape, size, color, purity, assay, composition, toxicity, etc. The auditor will evaluate product quality by comparing it with the product specifications filed with the regulatory agency.
Tips to Prepare for Quality Audit
Facing a quality audit for the first time may be overwhelming at first but it can be easily managed by following some simple tips. Below are some tips to make your journey easy.
Do What You Say and Say What You Do
Auditors scrutinize your documented processes and regulatory submissions to evaluate conformance. Therefore, you need to ensure that all your documented pieces of evidence are in line with the actual practices that you follow with your organization.
Don’t Change Without a Risk Assessment
In case you wish to deviate from the approved process for certain unforeseen situations, then you must do a risk assessment to study the impact of the deviation. You should only proceed to allow the deviation if the change does not result in a significant risk to patient health. A proper change control mechanism should be triggered to implement the change.
Check Your Internal Audit Report
Always take your internal audit report seriously and take necessary Corrective and Preventive Actions to address the findings in the internal audit report.
How Can an eQMS Help You in a Quality Assurance Audit
An eQMS is a great enabler to manage your audit data. It helps you keep organized for upcoming audits. Since all the data that you might need to show to the auditor is already available on the eQMS, you don’t need to run around to find the information. All the quality assurance documents such as SOPs, Work Instructions, Flowcharts, Risk Assessments, Deviations, CAPAs, and Change Controls are interlinked in an eQMS. Allowing your auditor to quickly glance at all the relevant documents on a single screen.
It also gives a lot of autonomy to the auditors as they navigate themselves through the system. The increased transparency helps in building the auditor’s trust. Additionally, an eQMS also enables you to carry out a remote audit of your facility allowing you and your auditor to work from anywhere in the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a quality assurance audit is crucial for ensuring conformance to regulatory requirements and guidelines. An internal audit can be a great tool to identify compliance gaps and improvement areas. Therefore, one can say, that a quality audit is like a compass that guides your organization to achieve excellence and accountability.
An eQMS streamlines and automates quality assurance practices from documentation to planning corrective and preventive actions. Thereby, it also reduces errors and improves the efficiency of your organization. Hence, when facing an audit, an eQMS can be your true companion.
Finally, there is nothing like passing and failing in a quality audit until you give up on improving your quality management practices to the satisfaction of the regulatory agency. Therefore, you must keep moving forward until you satisfactorily address the concerns of the regulatory agency.
Discover how a Smart QMS can help you get through any audit type successfully!